간 효소 변화, Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians
오늘 공부할 논문에서는 간 효소 수치의 변화를 해석하는 가이드를 제공한다.
1) 간의 기능적 해부학적 구조
2) 간 효소 변화에 대한 병리학
3) 접근법
간의 기능적 해부학적 구조
- 탄수화물, 단백질, 지질 대사에 중요한 역할
- 해독 장소 (ex 아미노산의 deamination 과정을 통한 urea 형성)
- 적혈구의 제거
- 담즙 분비
- lipoprotein, plasma protein, clotting factor 등의 합성
- glucose 재흡수 이후 glycogen으로 저장(glycogenesis)
- glucose 분비(glycogenolysis or glyconeogenesis)
간 효소 변화에 대한 병리학
| system or function |
marker | site or significance | function |
| 간세포 | Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) |
Liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, brain, red blood cell |
Catabolizes amino acids, permitting them to enter the citric acid cycle. |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) |
Liver | ||
| 쓸개즙정체 | Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |
Bone, intestine, liver, placenta |
Canicular enzyme that plays a role in bile production. |
| γ-Glutamyl- transpeptidase (GGT) |
ALP와 상관관계를 통해 간/담도 기원 여부 평가 | Catalyzes transfer of γ-glutamyl group from peptides to other amino acids. |
|
| Bilirubin | 간 또는 간 이외의 원인의 결과 상승 할 수 있음 | Breakdown product of hemolysis taken up by liver cells and conjugated to watersoluble product excreted in bile. |
|
| 간기능 | Serum albumin | Diet or liver | Liver synthesizes albumin |
| Prothrombin time | 비타민 K 관련 응고 인자로서 간에서 합성 | Bile salts are synthesized in the liver and necessary for vitamin K absorption |
- AST/ALT 값은 나이, 성별에 따라 다르므로 각각의 특성에 맞는 적합한 기준에 맞게 평가해야 한다. 예를 들어, 각 값은 격렬한 운동으로 증가할 수 있으며 건강한 사람을 대상으로 한 연구에서 입원 후 5% 에서 AST 증가를 17%가 ALT 증가를 경험하였다. (각 수치의 증가치 ; 0.4%–9.6% [95% CI], 9.1%–21.6% [95% CI]) 이는 제한된 움직임과 병원 식이에 의한 증가라고 생각된다.
접근법 : WHERE, WHEN, HOW
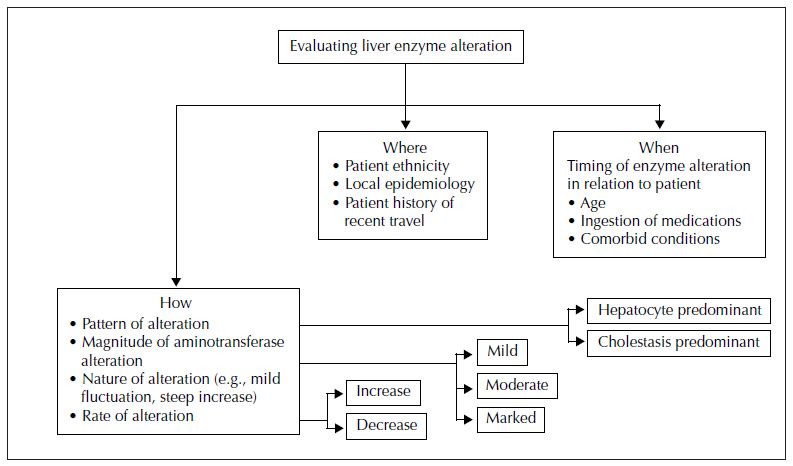
Where
- 병원에 내원한 환자에서의 간 효소 수치의 변화는 지리적 위치와 환자의 민족성에 따라 달라질 수 있음
- 해당 지역에서 간 질환의 국소 역학적인 특징이 서로 다름
ex) 간염 바이러스, 돌연변이에 의한 간경변 등
When
- 환자의 연령, 기저력, 약물 섭취와 관련된 간 효소 이상 발생 시기는 중요함
ex) Wilson's disease의 경우, 대개 어린 나이에 나타남
ex) 대부분의 약제가 간 효소 수치 이상을 유발할 수 있음
How
- 간 효소 변화 패턴은 원인에 따라 전형적인 패턴[하단의 그림 참조]처럼 보이기도 하지만 예외의 경우도 있음을 상기하자!
- 평가요소
- the predominant pattern of enzyme alteration (hepatocellular v. cholestatic)
- the magnitude of enzyme alteration in the case of aminotransferases (< 5 times, 5–10 times or > 10 times the upper reference limit, or mild, moderate or marked)
- the rate of change (increase or decrease over time)
- the nature of the course of alteration (e.g., mild fluctuation v. progressive increase)
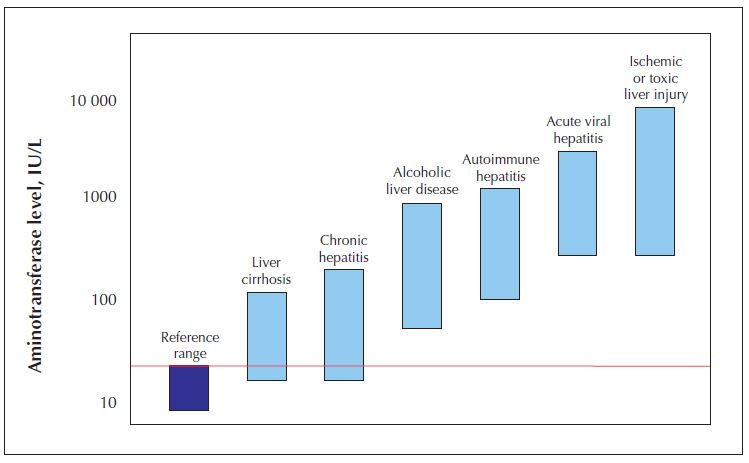
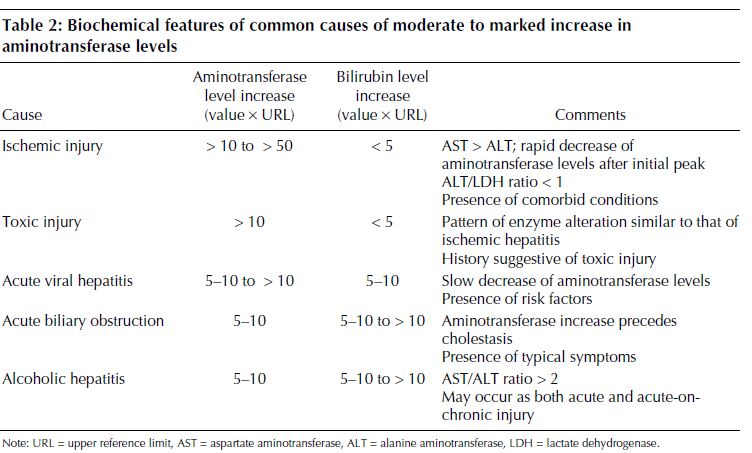
reference :
1) Giannini, Edoardo G., Roberto Testa, and Vincenzo Savarino. "Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians." Cmaj 172.3 (2005): 367-379.