loop계 이뇨제, furosemide, threshold, 역치, dose-response curve, Ceiling effect
Loop계 이뇨제
| 성분명 | onset time | duration | 반감기 | 상품명 |
| Furosemide | 0.5-1 hr | 6-8 hr | 0.5-2 hr 9 hr(ESRD) |
라식스 정 40 MG |
| - | 2 hr | 라식스 주 20 MG/2 ML | ||
| Torsemide | 1 hr 이내 | 6-8 hr | ~3.5 hr | 토르세미드 정 2.5 MG 토르세미드 정 5 MG 토르세미드 정 10 MG |
| Bumetanide | 0.5-1 hr |
4-6 hr | 1-1.5 hr | PO |
| 2-3 min | 2-3 hr | IV |
Loop계 이뇨제의 메커니즘
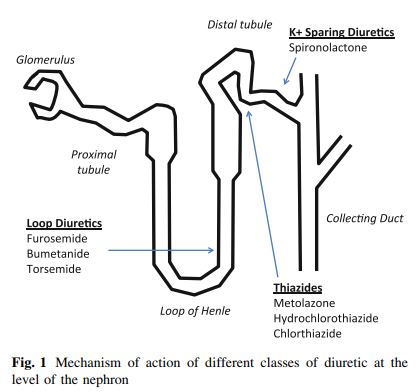
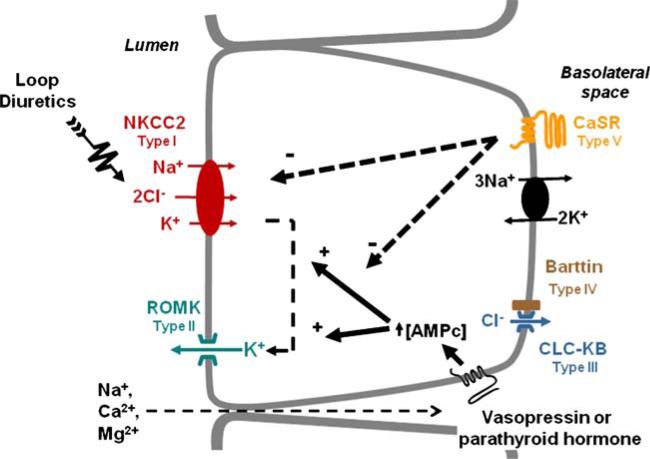
- thick ascending limb에서 여과된 Na의 25-30% 가량의 재흡수가 발생하기 때문에 이를 저해하는 loop계 이뇨제는 가장 강력한 이뇨 효과를 가짐
- loop계 이뇨제는 NKCC2(Na-K-2Cl cotransporter)에 작용하여 나트륨 재흡수를 억제하는데 이는 내강에 존재함
Furosemide
- protein binding 90%로 사구체를 통하여 여과되지 못함
- at 신장, furosemide + glucuronic acid(40-50%) 결합 → 50% free form 형태가 유기음이온수용체(OAT; organic anion transporter)을 통해 내강으로 분비/배설 → NKCC2 억제
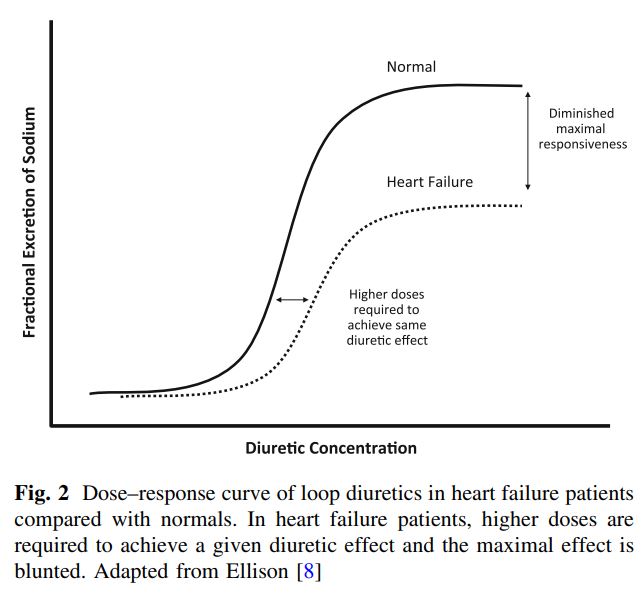
Loop계 이뇨제의 특징; Ceiling effect
- 이뇨 효과는 lumen에서의 free form furosemide에 의해 발생하는데 일정 수준의 농도에 도달하면 더 이상 이뇨효과가 강화되지 않음(ceiling dose)
- 반감기 1 hr → 시간이 지남에 따라 이뇨 효과 감소
- 따라서 원하는 이뇨 효과를 얻는 용량에 도달하게 되면 투여 용량 증가보다는 투여 빈도를 늘리거나 지속 정맥 주입요법이 더 효율적인 치료 방법임 (원하는 이뇨 효과를 얻기까지는 증량 필요함)
- 대부분의 loop계 이뇨제의 작용 시간이 짧기 때문에 염분 섭취가 충분히 제한되지 않을 때 postdiuretic salt retention은 이뇨 저항성을 유발하는 중요한 메커니즘 중 하나임 ⇒ 이뇨제 복용 간격을 줄여 극복 가능
5 : Brater DC. Diuretic therapy. N Engl J Med 1998;339:387-395
7 : Wilcox CS. New insights into diuretic use in patients with chronic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002;13:798-805
8 : Sarafidis PA, Georgianos PI, Lasaridis AN. Diuretics in clinical practice. Part I: mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects and clinical indications of diuretic compounds. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2010;9:243-257.
- 신기능이 저하된 상태에서도 이뇨 효과가 있으므로 GFR < 50 mL/min 이하로 감소된 환자에서 선택적 이뇨제로 사용됨
- 신기능 부전으로 내강에 도달하는 양이 감소함 ⇒ renal blood flow 감소 & endogenic organic anion의 증가로 인한 OAT acitivity 감소
- 간경변이나 울혈성 심부전의 경우 이뇨제에 대한 반응도가 감소 ⇛ 동일 효과를 위해 고용량 필요
👆주의
Ototoxicity may occur after rapid intravenous injection of a high dose of a loop diuretic, usually in patients receiving other ototoxic drugs, particularly aminoglycoside antibiotics. Hearing loss and tinnitus are usually transient.
The same daily dose caused excretion of a higher volume of urine and electrolytes when given as a continuous infusion. The maximal plasma furosemide concentration was significantly lower and this resulted in a reduced risk for ototoxic side effects. (즉, 고용량 투여 시 bolus보다는 continuous infusion 방법을 고려하라)
reference :
1) Gamba, Gerardo, and Peter A. Friedman. "Thick ascending limb: the Na+: K+: 2Cl− co-transporter, NKCC2, and the calcium-sensing receptor, CaSR." Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology 458.1 (2009): 61-76.
2) 전은실. "이뇨제 사용의 원칙과 실제." 대한내과학회지 80.1 (2011): 8-14.
3) De Bruyne, L. K. M. "Mechanisms and management of diuretic resistance in congestive heart failure." Postgraduate medical journal 79.931 (2003): 268-271.