경구 빈혈 치료제 첫 승인: FDA Approves Daprodustat, First Oral Anemia Treatment
FDA는 2023.02.01에 최소 4개월 이상 투석을 받은 성인의 경우 daprodustat(Jesduvroq)을 만성신장질환(CKD)으로 인한 빈혈 치료제로 승인했다.

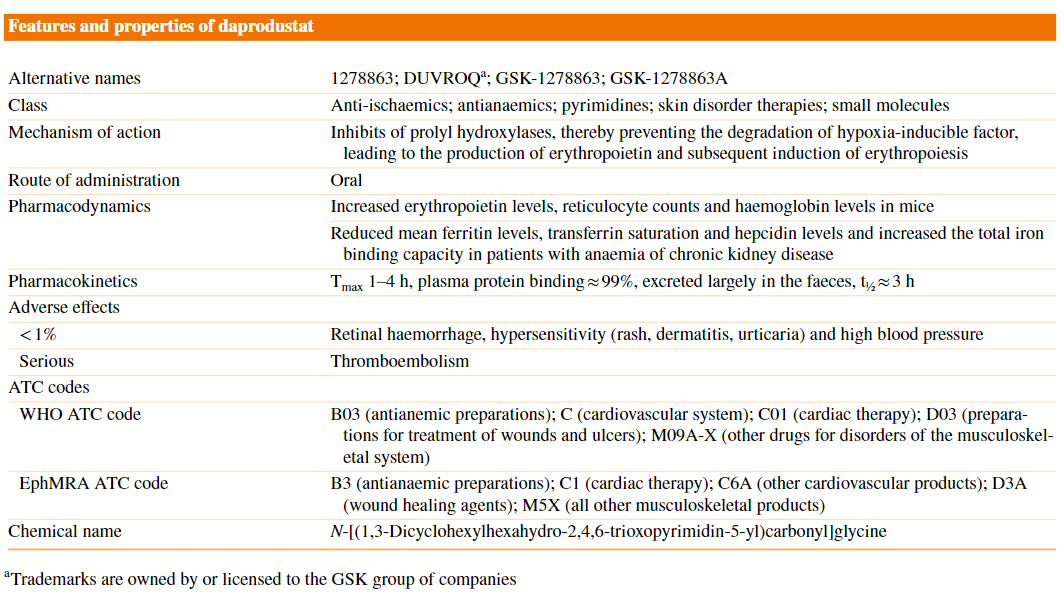
Daprodustat
경구용 저산소 유도 인자(HIF; hypoxia-inducible factor) prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
HIF를 안정화시켜 내인성 erythropoetin의 분비를 증가시키고 적혈구의 생성을 증가시킨다. 빈혈을 해결하기 위한 이 접근법은 높은 고도에 살고 있는 사람들에서 발생하는 생리적 효과에서 착안하였다.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of oral daprodustat are based on data from healthy subjects and a population pharmacokinetic analysis based on data from non-dialysis-dependent patients, haemodialysis patients and peritoneal dialysis patients with anaemia of CKD.
Daprodustat exhibited linear pharmacokinetics after single-dose administration over the dose range 10–100 mg.
| single oral 4 mg dose of daprodustat | |
| median tmax | 1.75 h (fasting state) or 2.75 h (after a meal) |
| food effect | after a standard CKD meal, as indicated by a 9% decrease in the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from 0 to infinity and an 11% decrease in the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) |
| multiple-dose administration | |
| median tmax | 1–3.25 h in healthy subjects receiving daprodustat 15–100 mg once daily 1–4 h in patients with anaemia of CKD receiving daprodustat 1–24 mg once daily |
| PK data | |
| Absolute bioavailability of daprodustat after oral administration of 6 mg | 65% |
| Volume of distribution after intravenous administration | 14.3 L |
| Protein bound | ≈ 99% (mainly albumin) |
| Metabolism | largely metabolized by CYP2C8 and to a small extent by CYP3A4 in in vitro studies → Mild (Child-Pugh A) or moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment also did not affect the pharmacokinetics of daprodustat. |
| The mean urinary excretion of oral daprodusta | < 0.05% of the dose |
| Excretion | primarily excreted in the faeces (73.6% of a radiolabelled dose), with renal excretion a secondary route of elimination (21.4%) → Moderate-severe renal impairment did not affect the pharmacokinetics of daprodustat to a clinically meaningful extent. |
빈혈 치료 : 헤모글로빈 수치 목표
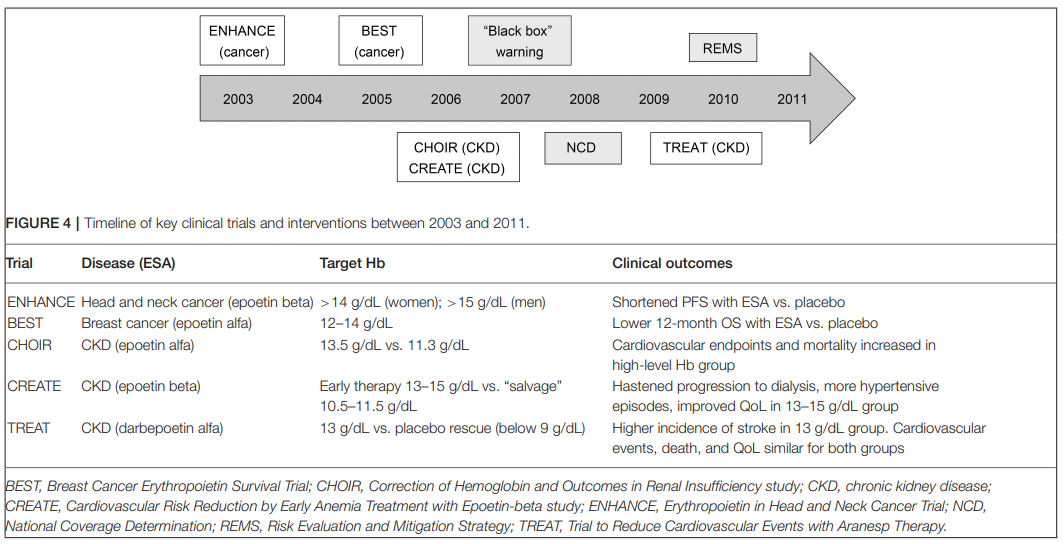
빈혈은 만성 콩팥병(CKD)의 흔한 합병증이다. CKD 환자의 빈혈에 대한 일반적인 치료법인 적혈구 자극제(ESA; erythropoiesis-stimulating agent)를 사용하여 헤모글로빈 수치를 13.0~14.0 g/dL로 증가되면 심혈관계 질환, 정맥혈전색전증, 사망 위험이 증가한 것으로 나타났다.
**너무 높은 Hb는 오히려 해롭다!!
2003~2011년 사이 각 적응증(암, 만성콩팥병)에 따른 중점 연구의 타임라인
🔥🔥 약제의 한계:
아직까지는 CKD를 가지고 있더라도 투석을 받지 않은 환자들에 의해 사용이 승인되지 않는다. 이러한 환자들을 위한 현존하는 유일한 치료 방법은 적혈구 생산의 자극제(ESAs) 또는 수혈이다.
reference:
1) uptodate
2) Medscape
3) Aapro, Matti, et al. "Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in the management of anemia in chronic kidney disease or cancer: a historical perspective." Frontiers in pharmacology 9 (2019): 1498.
4) Dhillon, Sohita. "Daprodustat: first approval." Drugs 80.14 (2020): 1491-1497.