오늘은 cyclic PN에 대해 공부를 해보자!
배경 :
parenteral nutrition의 가장 흔한 합병증으로 간부전(liver dysfunction)이 있다. 이를 예방/치료하기 위한 방법으로 cyclic parenteral nutrition(cyclic PN) 방법이 고려될 수 있다. 이는 말 그대로 24시간 내내 TPN 제제를 투여하는 것이 아닌 하루의 몇 시간은 투여되고 나머지 시간은 휴식기를 가지는 방법이다.
cyclic PN 투여시 투여되는 시간 동안은 다량의 fluid와 포도당 등의 영양소가 공급되므로 혈역학적으로 안정적인 상태인지 전해질이나 BST 등은 안정적인지가 고려 사항이 된다.
2002년에 발간된 삼성서울병원의 뉴스레터에서 다음과 같은 가이드라인을 제시하였다.
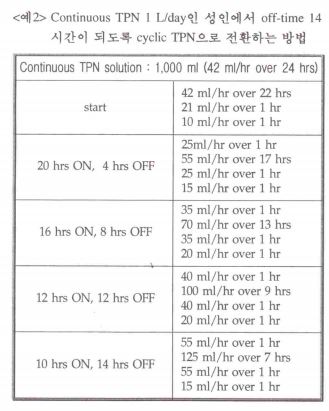
덧붙여 상태가 불안정한 중환자에게서는 혈당 조절과 전해질 및 수분 평형이 불안정하므로 연속 주입이 보다 안전하다고 소개하고 있다.
현재 심각한 영양불균형 상태인 환자에서의 TPN 도입이 아니라면 TPN 시작과 끝에 gradually 증량/감량 등을 하지 않고 있기에 중환자에서의 간 기능 보호를 위한 cyclic PN의 추가 근거를 조사 하였다.
[1] Effects of cyclic parenteral nutrition on parenteral-associated liver dysfunction parameters
- PN 관련 간부전으로 cyclic PN을 시작한 18세 이상 성인 환자(n=31)
- cyclic PN 도입 전/후의 LFT 비교(aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and total bilirubin (TB))
PN regimen(2002 ASPEN, 2009 ESPEN 기준) :
- glucose <5g.kg.day
- lipid <1.5 g/kg/day
기준 :
liver dysfunction (LD) was defined as:
- Cholestasis: alkaline phosphatase (ALP) > 280UI/L, gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) > 50UI/L or total bilirubin (TB) > 1.2 mg/dL
- Hepatic necrosis: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > 40UI/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) > 42UI/L
- Mixed pattern: ALP > 280UI/L, GGT > 50UI/L or TB > 1.2 mg/dL plus AST > 40 IU/L or ALT > 42UI/L
exclusion : severe liver disease evidenced by abnormal biochemical hepatic parameters, a history of renal failure, death during treatment or a duration of cPN ≤ 4 days
- study period 동안 총 557명의 환자가 PN을 받았으며 그중 56명이 cyclic PN 처방이 났음. 그 중 37명이 inclusion criteria를 만족함
(continuous PN → cyclic PN으로 처방 변경)
| continuous PN | cyclic PN | |
| 투여기간 | 15.2 ± 11.2 days | 12.8 ± 12.7 days (range 3 to 42 days) |
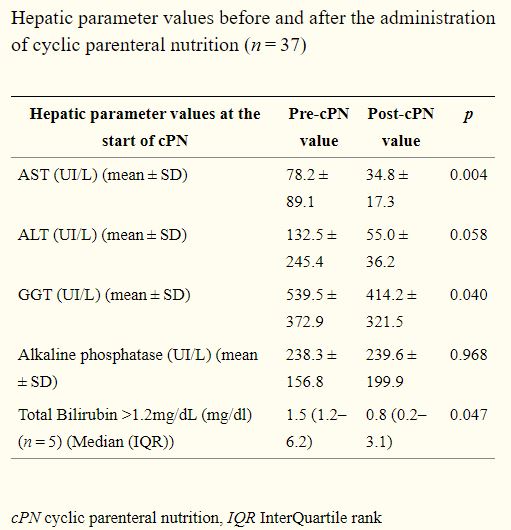
결과 : ALP를 제외한 간 기능 수치는 cyclic PN을 시작 전/후 임상적으로 유의한 차이를 보임(p <0.05)
결론 : cyclic PN으로 PN 관련 간부전의 AST, GGT, TB의 수치를 유의하게 정상화시킬 뿐만 아니라 ALT 역시 정상화 가까운 수치로 감소시킴. PN 관련 간부전 환자에서 cyclic PN의 도입을 고려할 수 있음
😅 한계 : 중환자를 대상으로 한 연구가 아닌 점, severe hepatic disease는 제외된 점
[2] Cyclic parenteral nutrition infusion: considerations for the clinician
continuous PN infusion을 투여받던 성인 환자에서 hepatobiliary dysfunction 발생 시 cyclic infusion으로 전환 고려해볼 수 있음
* hepatobiliary dysfunction 발생 : total bilirubin 5-20 mg/dL
unselected clinical population에서 PN 투여 시 continuous PN에서 cyclic PN으로 변경으로 ALP, LDH 감소가 관찰되었음 [3]하지만 기저치의 빌리루빈 수치의 상당한 증가가 없는 상태에서 regimen 변경에 따른 빌리루빈 수치 호전에 대한 근거는 부족함
기계 환기를 적용한 중환자에서 cyclic PN은 continuous PN보다 energy expenditure↑ & O2 uptake↑ & CO2 제거 ↑[4]
The lower nutrient-induced thermogenesis and more positive energy balance, indicates a more efficient utilisation of nutrients during continuous than during cyclic TPN. The lower CO2 production during continuous TPN, may be advantageous when respiratory function is compromised. The plateau in energy expenditure in response to TPN infusion may be useful as a guideline for nutritional therapy.
결론 : Critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients may be better candidates for continuous PN infusion than cyclic due to increased carbon dioxide production and reduced apparent metabolic efficiency with the latter. Other theoretical concerns in these patients include the potential for disruption of hemodynamic stability, and interference with intensive insulin therapy.
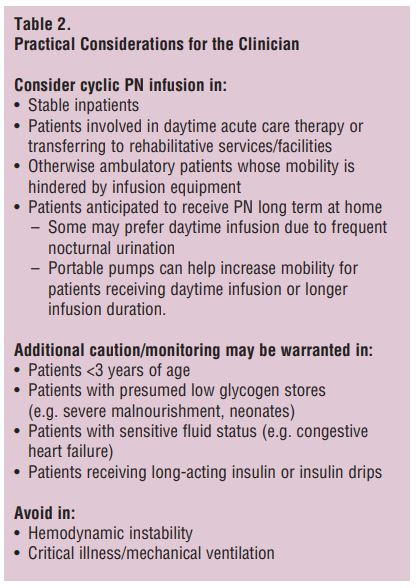
😃 결론 :
아직까지 중환자에서의 cyclic PN을 시도하기에 근거는 부족한 것으로 판단됨.
하지만 중환자실에 재원 중이더라도 혈역학적/혈당 조절이 안정적인 환자에서 PN associated liver dysfunction 시, cyclic PN을 고려해볼 수 있겠음.
reference:
(1) Villafranca, Jose J. Arenas, et al. "Effects of cyclic parenteral nutrition on parenteral-associated liver dysfunction parameters." Nutrition journal 16.1 (2017): 66.
(2) Cober, M. Petrea, and Stephen Marc Stout. "Cyclic parenteral nutrition infusion: considerations for the clinician." Practical Gastroenterology (2011): 11.
(3) Maini, B. G. B. J. T. A. P. B., et al. "Cyclic hyperalimentation: an optimal technique for preservation of visceral protein." Journal of Surgical Research 20.6 (1976): 515-525.
(4) Forsberg, E., et al. "Metabolic and thermogenic response to continuous and cyclic total parenteral nutrition in traumatised and infected patients." Clinical Nutrition 13.5 (1994): 291-301.
'👩⚕️Px 영역 > TPN·영양' 카테고리의 다른 글
| essential fatty acid, 필수 지방산, triene/tetraene ratio (0) | 2020.12.20 |
|---|---|
| Parenteral nutrition 투여와 pancreatic enzyme 상관 관계 (0) | 2020.12.09 |
| TPN abrupt discontinuation, TPN 중단, tappering? (0) | 2020.11.11 |
| 급성 신부전 환자에서의 영양, AKI, nutrition (0) | 2020.10.29 |
| 헤파타민, BCAA, 간장애 환자에게 효과가 있을까? (0) | 2020.09.10 |


댓글