[1] Is Opioid Addiction a Sufficient Predicting Factor for Common Bile Duct Dilatation? A Sonographic Study
In the absence of hepatobiliary symptoms, opioid consumption has been shown to cause dilatation of the common bile duct (CBD). The main objective of this study was to measure with sonography CBD diameters in opioid addicts as compared with non-addicts.
대조군의 평균 CBD 직경은 4.13 ± 1.14 mm이었으며 마약 중독자 군은 8.16 ± 2.54 mm로 증가된 것을 알 수 있다. 모든 연령대에서 dilatation of the CBD이 관측되었고 특히 경구 투여가 가장 CBD 확장 효과가 컸다.
[2] opioid의 허가사항
morphine의 국내 허가사항 중 주의사항
담낭질환, 담석이 있는 환자(담도 경련이 나타날 수 있다.)
tramadol의 warnings/precautions
Biliary tract impairment: Use caution in patients with biliary tract dysfunction or acute pancreatitis; opioids may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
[3] ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03870347
Opiate Use and Biliary Dilation(담도 확장)
빌리루빈 < 2 mg/dL인 환경에서 opioid 사용과 담도 확장 사이의 연관성을 내시경 초음파를 통해 평가하기 위한 임상 시험(prospective study)이다. 정확한 평가를 위해 common bile duct과 pancreatic duct diameter를 측정하고 담도 확장을 조절할 수 있는 기타 non-obstructive factor 요인(i.e. age, cholecystectomy status, duration and type of opiate used)을 식별했다.
목적 : as it provides additional data for interpretation of isolated common bile duct dilation in asymptomatic patients.
Actual Study Start Date : January 3, 2018
Estimated Primary Completion Date : January 2021
Estimated Study Completion Date : January 2022
[4] sciencedirect.com
- Opioid receptor agonist와 biliary tract 효과
opioid의 치료 용량은 Oddi 괄약근(the sphincter of Oddi)을 수축시키고 담도 압력(biliary tract pressure)을 10배나 증가시킨다. 담석 산통(biliary colic; 담석에서 볼 수 있는 우상복부의 격통) 환자의 경우 morphine 투여 후 통증이 더 악화될 수 있다. 마찬가지로 fentanyl, morphine, and dextropropoxyphene은 담도 경련(bile duct spasm)을 유발할 수 있다.
“It is standard teaching that morphine should not be used to treat patients with pancreatitis because it causes a rise in biliary and pancreatic pressure”
이러한 이유로 췌장염 환자에게 morphine 사용으로 담관 질환이 없는 환자에서도 biliary colic를 유발하기 때문에 meperidine(pethidine)이 진통제로 선택된다.
Oddi 괄약근의 수축과 괄약근의 기저 톤(tone)과 수축 위상(phasic contraction)의 빈도는 ERCP(endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)를 통해 측정되었으며 기저톤의 증가가 괄약근 부전의 가장 좋은 지표로 여겨진다.
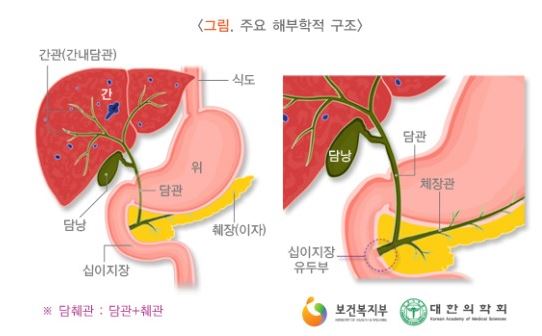
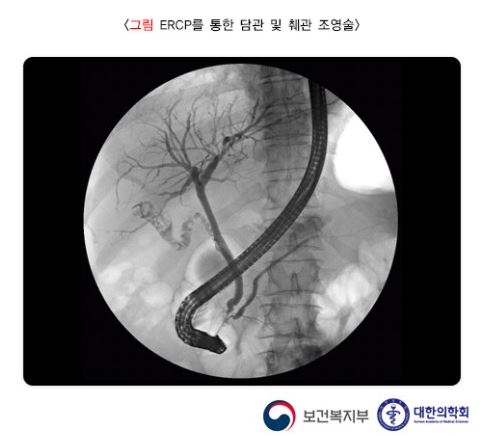
cf) ERCP: 내시경을 십이지장까지 삽입하여 십이지장의 유두부에 작은 구멍을 통하여 담관 및 췌관에 조영제를 주입시켜 병변을 관찰하는 검사법
| 성분명 | 용량 | Contraction | Basal pressure |
| Morphine sulfate | 2.5–5 mcg/kg | 증가 | 변화 없음 |
| Morphine sulfate | 10 mcg/kg | 증가 | 증가 |
| Pethidine | - | 증가 | 변화 없음 |
| Tramadol | - | - | 변화없음 |
| Buprenorphine | - |
- |
변화없음 |
* Pethidine and tramadol have less effect on the gastrointestinal tract than equi-analgesic doses of morphine.
* The antagonist naloxone 0.4 mg intravenously had no effect alone on the sphincter basal pressure and did not stop the increase in pressure caused by morphine. However, case reports have suggested that naloxone reduces sphincter spasm in clinical situations.
- Impact of Acute and Chronic Bile Duct Obstruction on Liver Blood Flow
담관 폐쇄는 간혈류에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 일반적으로 만성 담도폐쇄가 있을 때 간혈류가 감소되며 간부전으로 이어진다. 반대로 조기 폐쇄(eraly obstruction)로 담관 압력이 급성 증가로 반사적으로 간혈류의 증가가 유발될 수도 있다. 만성 담도 폐쇄 환자의 약 20%가 임상적으로 유의한 간문맥 고혈압이 있다.
- Bile secretion and pathophysiology of biliary tract obstruction
간세포로 이루어진 plates 부분에서 간문맥에서 시작하여 중심 정맥 방향으로 혈류가 흐른다. 이 plates는 1차적으로 담즙이 생성되는 부위이다. 생성된 담즙은 small ductules에서 larger ducts으로 흐른다. 담관 폐쇄가 발생하였을 때 bile canaliculi가 확장되고 microvilli 가 파괴된다.

Biliary system의 정상적인 압력은 5 to 10 cm H2O으로 낮은 압력을 가진다. 하지만 완전 혹은 부분 담도 폐쇄의 경우 담관 압력이 30 cm H2O까지 증가된다.
담도 폐쇄로 인해 섬유화가 발생하여 구조적 영향을 끼친다. 이뿐만 아니라 담도 압력 상승으로 간세포에 의한 담즙 생성을 변화시킨다.
In the setting of biliary obstruction and elevated biliary pressure, bile becomes less lithogenic because of a relative decrease in cholesterol and phospholipid secretion compared with bile acid secretion. With the relief of biliary obstruction and the normalization of biliary pressures, the recovery of cholesterol and phospholipid secretion is more rapid than bile acid secretion; therefore bile is more lithogenic in this setting. This phenomenon may lead to premature occlusion of decompressive bilary stents placed for the management of obstructive jaundice.
황달 환자의 경우 담관으로 배설되는 약제의 배설능이 감소된다. 폐쇄성 황달로 인한 담즙 농도의 증가는 hepatic cytochrome P450의 억제되어 oxidative metabolism의 속도가 감소된다. 뿐만 아니라 비정상적인 고농도 담즙은 apoptosis를 유발한다. 또한 간세포의 합성 능력도 감소시키기 때문에 알부민, 응고 인자, 분비 면역글로불린 등의 감소가 유발된다.
[5] Chronic Extrahepatic Bile Duct Dilatation: Sonographic Screening in the Patients with Opioid Addiction
한편, Odi의 괄약근 경련은 오피오이드의 중요한 효과 중 하나로 알려져 있으며, 중독된 개인에서 이 괄약근의 장기 경련은 결과적으로 담도 정체와 CBD의 확장을 유발할 수 있다.
However, it should be remembered that all narcotics increase the internal pressure of biliary ducts, but the biggest increase is with morphine.
[6] Narcotic analgesic effects on the sphincter of Oddi: a review of the data and therapeutic implications in treating pancreatitis.

No outcome-based studies comparing these drugs have been performed in patients with acute pancreatitis. Morphine may be of more benet than meperidine by offering longer pain relief with less risk of seizures. No studies or evidence exist to indicate that morphine is contraindicated for use in acute pancreatitis.
[7] Paradoxical pain from opioids: increased risk of acute pancreatitis
opioid는 췌장염과 밀접한 연관이 있다. opioid는 급성 혹은 만성 췌장염의 통증 조절에 일반적으로 사용되지만 역설적으로 opioid가 급성 췌장염 유발 위험이 있다고 여겨진다. opioid abuse군에서 급성 췌장염 발생과 관련된 여러 사례가 있었으며, opioid abuse군의 oddi 기능 장애에 기인한 담관 확장 등이 그 예다.
Although cholecystectomy is assumed to reduce the risk of acute pancreatitis, the authors note a 1.1 per 1,000 person-year risk of pancreatitis, which is ~ 2–3 times higher than the incidence noted in previous studies from the United States. Here it is important to realize a major limitation that they partly acknowledge, which is that other important causes of pancreatitis such as undocumented alcoholism, common bile duct stones, and undiagnosed idiopathic pancreatitis may have been missed by the study design, especially since these conditions can lead to or be associated with higher opiate use.
This point is further reinforced by the lack of evidence supporting pancreatic sphincter of Oddi dysfunction as a cause of pancreatitis in this study, and the strong society guidelines that recommend exclusion of other causes before attributing pancreatitis to sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.
Since common bile duct pressures can be elevated after cholecystectomy, a post-hoc analysis of effect of sphincterotomy (which was excluded) on the risk of post-cholecystctomy pancreatitis may have helped. This is relevant to the hypothesis and conclusions of the study since sphincterotomy would be an antidote for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and hypothetically should reduce the risk of AP even with narcotic use.
In summary, the study by Kim et al is provocative by providing evidence that codeine-induced pancreatitis likely does exist, possibly due to sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. The study also opens the need for more systematic and larger studies in which the risk of pancreatitis from commonly-used opioid agonists such oxycodone, hydrocodone, tramadol, and more recently eluxadoline can be studied while taking into account the impact of sphincterotomy on post cholecystectomy pancreatitis.
reference:
1) https://www.sciencedirect.com/ : bile duct pressure
2) ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03870347
3) Farahmand, Habib, M. PourGholami, and M. Sheikh Fathollah. "Chronic extrahepatic bile duct dilatation: sonographic screening in the patients with opioid addiction." Korean journal of radiology 8.3 (2007): 212-215.
4) Rezaee, Ahmad, et al. "Is opioid addiction a sufficient predicting factor for common bile duct dilatation? A sonographic study." Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 26.3 (2010): 137-142.
5) Thompson, Donald R. "Narcotic analgesic effects on the sphincter of Oddi: a review of the data and therapeutic implications in treating pancreatitis." The American journal of gastroenterology 96.4 (2001): 1266-1272.
6) Singh, Vijay P. "Paradoxical pain from opioids: increased risk of acute pancreatitis." (2020): 13-14.
'🤹♂️ 카테고리별 약물 > 진통·진정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Dexmedetomidine vs Propofol: 약제별 특성 비교(comparison) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
|---|---|
| 듀로제식 디트랜스(Durogesic D-trans patch): 잘라서 사용 가능? 절단 가능? (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome: 벤조다이아제핀 금단 현상 약물 치료 (0) | 2021.07.11 |
| 금단 현상: 외상 환자에서의 opioid/benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrom (0) | 2021.07.08 |
| IV PCA 안정성(stability): 언제까지 보관할 수 있을까? (0) | 2021.06.16 |


댓글