1. Pain
1) mild/moderate pain
- 1st-line: Acetaminophen, NSAIDs
2) moderate/severe pain
- 1st-line: IV opioid
if renal dysfunction: consider fentanyl
- 2nd-line: improved pain control and opioid sparing
Acetaminophen, NSAIDs, Alpha-2 agonist
관련 Recommendation
| We recommendthe addition of an adjunct NSAID (IV or oral) toimprove early postoperative analgesiain critically ill pediatric patients. | Strong | Moderate |
| We suggest the addition of an adjunct NSAID agent (IV or oral) to decrease opioid requirements in the immediate postoperative period in critically ill pediatric patients. | Conditional | Low |
| We suggest the addition of adjunct acetaminophen (IV or oral) to improve early postoperative analgesia in critically ill pediatric patients. | Conditional | Low |
| We suggest the addition of adjunct acetaminophen (IV or oral) to decrease opioid requirements in the immediate postoperative period in critically ill pediatric patients. | Conditional | Low |
TABLE: Opioid Analgesics
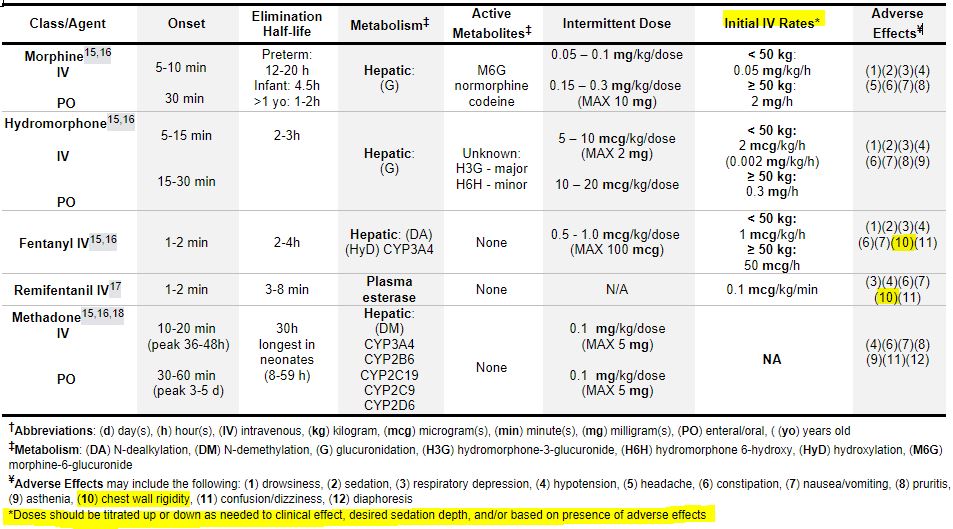
소아 중환자에서 IV opioid 사용이 진통의 질을 높이는 것은 데이터로 입증되지 않았다. 미국, 캐나다, 영국의 PICU 관행 조사에서 morphine이 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 진통제이며 그다음이 fentanyl이라 보고하였다.
morphine은 다른 약제에 비해 pruritis(가려움증)나 urinary retention(소변 저류) 부작용의 발생률이 높았지만 nausea(오심)나 장폐색(ileus) 부작용의 발생률은 비슷하였다.
IV opioid를 사용할 때 호흡부전(respiratory depression), 저혈압(hypotension), 흉부 경직(rigid chest syndrome; 특히 합성 opioid에서)과 같은 중증의 부작용을 주의해야 한다.
특히 신기능 장애 환자에서 morphine과 hydromorphone의 활성 대사물이 축적되어 효과 지속 기간이 연장될 수 있으므로 주의해야 한다.
fentanyl(remifentanil 역시)의 경우 신기능 장애 환자에서 가장 선호되는 opioid일 수 있다.
remifentanil의 경우 대사 경로가 간을 거치지 않고 plasma esterase이기 때문에 간장애 환자에서 축적될 가능성이 낮은 약제로 평가되며 실제 성인 중환자에서 많이 사용되고 있다. 하지만 소아 중환자에서 remifentanil의 사용은 빠른 내성(rapid tolerance)과 반발성 통증(rebound pain with synthetic opioids)에 대한 우려가 있다.
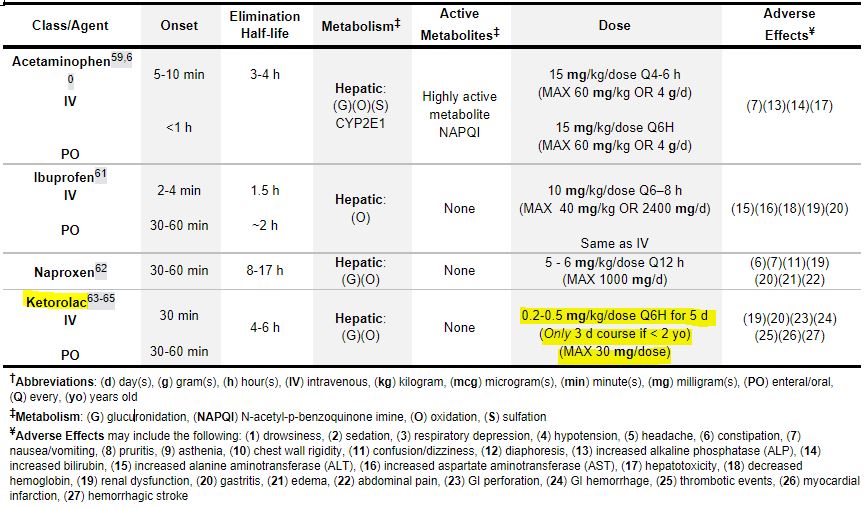
TABLE: Non-opioid Analgesics
2. Sedation
1) 1st-line: Alpha 2-agonist(post-OP & cardiac patients)
2) 2nd-line: Ketamine, propofol, BZD(if consider delirium)
관련 Recommendation
| We suggest the use of alpha2-agonists as the primary sedative class in critically ill pediatric patients requiring MV. | Conditional | Low |
| We recommend that dexmedetomidine be considered as a primary agent for sedation in critically ill pediatric post-operative cardiac surgical patients with expected early extubation. | Strong | Moderate |
| We suggest the use of dexmedetomidine for sedation in critically ill pediatric postoperative cardiac surgical patients to decrease the risk of tachyarrhythmias. | Conditional | Low |
| We suggest that continuous propofol sedation at doses less than 4 mg/kg/hr (67 µg/kg/min) and administered for less than 48 hr may be a safe sedation alternative to minimize the risk of propofol-related infusion syndrome development. | Conditional | Low |
| Short term (< 48 hr) continuous propofol sedation may be a useful adjunct during the periextubation period to facilitate weaning of other analgosedative agents prior to extubation. | Good practice | |
| We suggest consideration of adjunct sedation with ketamine in patients who are not otherwise at an optimal sedation depth. | Conditional | Low |
TABLE: Pharmacology of Sedative Medication
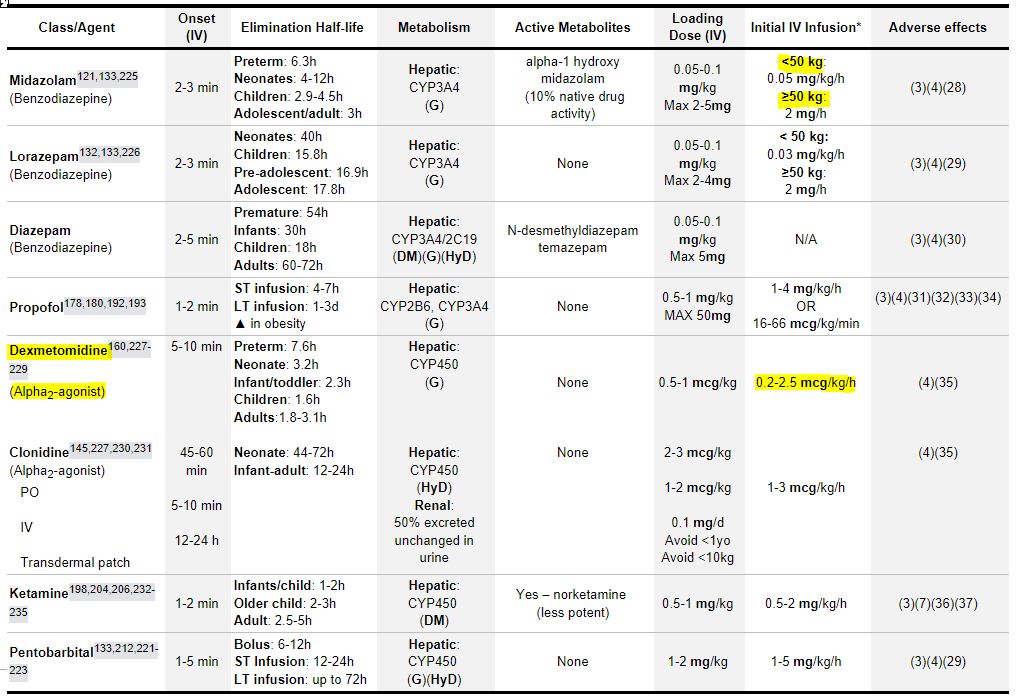
전 세계적인 조사 기반 연구에서는 BZD가 가장 일반적으로 처방되는 약제임을 보였지만, 최근 몇 년 동안 다른 약제들들은 신경독성과 BZD의 섬망 발생 위험 때문에 alpha-2 agonist의 사용이 증가되고 있다.
Benzodiazepines(BZD)
Their primary clinical effects include dose-dependent anxiolysis, sedation, and anterograde amnesia in addition to potent anticonvulsant effects
midazolam과 lorazepam이 가장 흔히 사용되는 IV BZD이다. 하지만 lorazepam의 경우 propylene glycol이 함유되어 있으므로 continuous infusion 시에는 midazolam이 선호된다.
하지만 midazolam의 활성형 대사체로 인해 신기능 장애 환자에서 주의가 필요하다.
위의 table에도 명시되어 있듯이 어린 환아일수록 clearance가 감소(반감기 연장)되므로 호흡 부전 부작용에 각별한 주의가 필요하다. 또한 cardiorespiratory depression은 opioid와 병용 시 극대화될 수 있다.
iatrogenic withdrawal syndrome(IWS)에 유의한다.
Alpha2 adrenergic receptor agonists (Alpha2-agonists)
중추의 alpha2 adrenergic receptor 작용에 의해 진통/진정 작용이 나타난다. 투여 초기 말초의 alpha2 adrenergic receptor 작용에 의해 고혈압이 발생할 수 있으며, 이후 중추에서 매개되는 교감 작용(centrally mediated sympatholysis)이 우세해지면서 dose/duration-dependent 서맥 and/or 저혈압이 발생할 수 있다.
특히나 다른 약제들에서 흔히 보이는 호흡부전 효과가 약하다는 장점이 있다. 하지만 epileptiform activity 억제 효과도 없다. 신기능 부전 환자에서는 용량 조절이 필요 없지만 간 기능 부전 환자에서는 용량 조절이 필요하다.
다른 약제처럼 장기간의 사용은 내성 발생과 IWS과 관련이 있다.
Propofol
진통 효과는 없지만 anticonvulsant & anti-emetic 효과는 가지고 있다.
dose dependent respiratory depression or apnea, loss of airway protective reflexes, hypotension as a result of myocardial depression and/or vasodilation, and the development of Propofol-Related Infusion Syndrome (PRIS) 부작용을 가진다.
약제의 친유성 성질로 특히 비만 환자에게서 또는 장기간 사용 시 상당량이 지방에 축적될 수 있다.
Tolerance and IWS to propofol have not been described.
Ketamine
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA) antagonism이며 potent analgesic, anxiolytic/sedative, and anterograde amnestic 효과를 가진다. 교감신경 유사 작용(sympathomimetic properties)이 있기 때문에 심혈관계 기능을 보존 효과를 기대할 수 있지만 심각한 심근 질환이나 카테콜아민 결핍 상태(catecholamine-depleted state)에서는 효과를 발휘하지 못할 수 있다.
고용량에서도 호흡부전 효과는 잘 나타나지 않으며(오히려 기관지 확장 효과가 있음) PICU에서 non-intubated patient에서 인기 있는 진통/진정제이다.
Its bronchodilating effects have made it attractive for use as a continuous infusion in patients with lower airway obstruction either prior to or during invasive MV
중요한 부작용으로는 hypersalivation which may trigger laryngospasm & emergence delirium이 있으며 폐고혈압이나 안압 상승이 의심되는 환자에서 투여할 때는 주의해야 한다.
reference:
1) Smith, Heidi AB, et al. "2022 society of critical care medicine clinical practice guidelines on prevention and management of pain, agitation, neuromuscular blockade, and delirium in critically ill pediatric patients with consideration of the ICU environment and early mobility." Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 23.2 (2022): e74-e110.
2) Beckman, Elizabeth J., M. L. Buck, and K. B. Manasco. "Analgesia and sedation in hospitalized children." PedSAP Book 3: Sedation and Analgesia (2017): 7-30.
'🤹♂️ 카테고리별 약물 > 진통·진정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Multimodal analgesia 전략(non-opioid analgesia): gabapentin 안전한 약물인가 (0) | 2022.11.09 |
|---|---|
| 마약성 진통제(opioid) 복용 방법: 급성기 통증, 펜토라 박칼정 & 앱스트랄 설하정 (0) | 2022.08.14 |
| 2021 성인중환자실에서 통증, 진정, 섬망, 부동화 및 수면장애 예방의 임상 진료지침 (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| 듀로제식 패치에서 fentanyl은 얼마만큼의 방출될까? (0) | 2021.09.09 |
| Dexmedetomidine vs Propofol: 약제별 특성 비교(comparison) (0) | 2021.09.01 |


댓글