일반적으로 beta blocker(BB)의 부작용 중 당뇨환자에서 저혈당 혹은 저혈당 증상을 은폐가 있다.
BB가 β2에도 영향을 줌으로써 glucose metabolism에 영향을 주게 된다. (β2 차단에 따른 glycogenolysis 억제)
따라서 selectivity가 있는 BB의 경우 상대적으로 대사 부작용이 적을 것이다. (이론적으로)
DM type에 따른 BB의 혈당 부작용 차이[1]
| insulin-dependent diabetic | noninsulin-dependent diabetic |
| beta-blockers can prolong, enhance, or alter the symptoms of hypoglycemia |
beta-blockers can potentially increase blood glucose concentrations and antagonize the action of oral hypoglycemic drugs. |
Hypoglycemia와 BB의 상관관계[2]
Do betablockers have adverse effect on blood glucose metabolism?
- β1 selective BB의 경우 대사 부작용이 없을 것이라 예상되지만 실제 보고된 경우가 있음
- 이론적으로는 대사 부작용이 적을 것으로 예상됨
- 체중 변화에 따라 포도당 내성과 인슐린 민감도가 영향을 받을 수 있기 때문에 고혈압 치료제(BB를 포함)의 구체적인 대사 효과(혹은 부작용)를 입증하는 것은 매우 힘듦
- 따라서 BB 복용을 한다면 환자에게 체중 유지 관리에 대한 적절한 교육이 필요함
- 체중 유지가 되는 경우, selective BB는 혈당 혹은/그리고 인슐린 민감도에 영향을 미치지 않음
Do betablockers mask symptoms of hypoglycaemia?
- 이론적으로 저혈당시 발생할 수 있는 adrenergic counterreaction(반작용)을 은폐함
ex. 떨림, 빈맥, 발한(most)
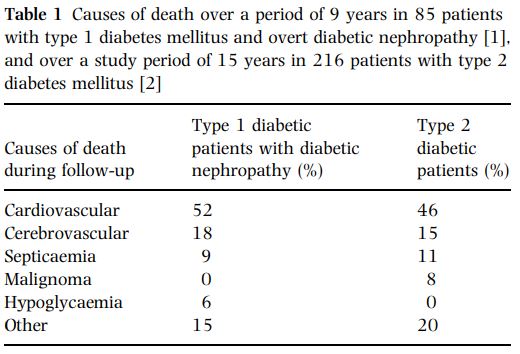
- 특히 1형 당뇨환자에게 매우 중요함(1형 당뇨환자에게서 저혈당이 더 빈번하고 cause of death까지 이르기 때문)
- Hence, betablockers do not mask hypoglycemia but may change the pattern of symptoms by increasing the occurrence of sweating. No study has ever reported an increased risk of severe hypoglycaemia associated with betablocker treatment of diabetic patients. Even amongst patients prone to hypoglycaemia and amongst individuals with low levels of glycosylated haemoglobin betablockers do not increase the hypoglycaemic risk.
결론적으로 (선택성) BB가 혈당에 끼치는 영향은 미미함
선택성/비선택성 BB에 따른 hypoglycemia 차이[3]
- randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial
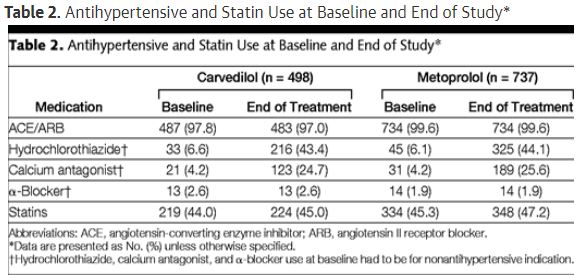
- 2001~2004년 동안 carvedilol과 metoprolol의 glycemic control 차이
- 36-85세 고혈압과 2형 당뇨환자를 대상으로 35주간 추적 관찰함
| carvedilol group | metoprolol group | |
| N | 498 | 737 |
| dose | 6.25-25 mg bid | 50-200 mg bid |
| mean doses required to achieve target BP |
17.5 mg bid | 128 mg bid |
| mean (SD) HbA1c | 0.02% [0.04%]; P = .65 | 0.15% [0.04%]; P<.001 |
| Insulin sensitivity | –9.1%; P = .004 | –2.0%; P = .48 |
- 두 그룹 간의 기저치에서 HbA1c의 평균 변화는 차이가 있었음 (0.13%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.22% to –0.04%; P = .004; modified intention-to-treat analysis)

- 결론 : 두 BB모두 내약성이 좋았음; RAS(renin-angiotensin system) 억제제와 carvedilol 병용 시 혈당 조절에 유의한 영향을 끼치지 못했으며 metoprolol 군에 비해 대사적으로 이점이 있었다.
Drug induced hyperglycemia [4]
In people with diabetes, β-blockers such as propranolol, metoprolol, and atenolol can result in consistently elevated fasting blood glucose levels. In a recent study, atenolol was also shown to contribute to new-onset diabetes and to worsen hyperglycemia in people with abdominal obesity. In this study, adverse metabolic effects, including the development of hyperglycemia manifesting as impaired fasting glucose, were apparent within 9 weeks of therapy initiation.
β-blockers are thought to contribute to the development of hyperglycemia by impairing the release of insulin from the pancreatic β-cell. Interestingly, carvedilol and nebivolol are not associated with the development of hyperglycemia or new-onset diabetes.
⇛ 하지만 국내 허가사항상 nebivolol의 시판 후 조사에서 이 약과 인과관계를 배제할 수 없는 약물 유해반응 발현율로 혈당 상승이 0.4%(3건)이 보고되었음
⇛ carvedilol도 국내 허가사항상 이상반응에 고혈당이 명시되어 있음
Drug induced hypoglycemia [5]
β-blockers can cause or exacerbate hypoglycemia in some individuals, either by worsening an already present hypoglycemic episode or by delaying recovery time. The mechanism responsible for β-blocker–induced hypoglycemia involves inhibition of hepatic glucose production, which is promoted by sympathetic nervous stimulation. In addition, adrenergic counterregulation is diminished, resulting in a reduction in glycogenolysis.
Non-cardioselective β-blockers such as propranolol are more likely to cause hypoglycemia than cardioselective ones such as atenolol and metoprolol. Nevertheless, patients on the latter should still be cautioned about the potential for drug-induced hypoglycemia.
Furthermore, β-blockers have the potential for masking symptoms of hypoglycemia. The catecholamine-mediated neurogenic hypoglycemic symptoms masked by this class of medications include tremor and palpitations. Hunger, tremor, irritability, and confusion may be concealed as well. Sweating, however, remains unmasked and may be the only recognizable sign of hypoglycemia in individuals treated with β-blockers.
결론 : 선택성/비선택성 BB 모두 hypoglycemia를 주의! 뿐만 아니라 hyperglycemia도 주의하자!
reference :
(1) Mills, Gregory A., and John R. Horn. "β-blockers and glucose control." Drug intelligence & clinical pharmacy 19.4 (1985): 246-251.
(2) Sawicki, P. T., and A. Siebenhofer. "Betablocker treatment in diabetes mellitus." Journal of internal medicine 250.1 (2001): 11-17.
(3) Bakris, George L., et al. "Metabolic effects of carvedilol vs metoprolol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: a randomized controlled trial." Jama 292.18 (2004): 2227-2236.
(4) Rehman, Abdur, Stephen M. Setter, and Mays H. Vue. "Drug-induced glucose alterations part 2: drug-induced hyperglycemia." Diabetes Spectrum 24.4 (2011): 234-238.
(5) Vue, Mays H., and Stephen M. Setter. "Drug-induced glucose alterations part 1: drug-induced hypoglycemia." Diabetes Spectrum 24.3 (2011): 171-177.
'🤹♂️ 카테고리별 약물 > 심혈관' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자렐토 정, rivaroxaban, 자렐토 정 2.5 MG, 허가사항, 적응증 (0) | 2020.11.29 |
|---|---|
| 자렐토 2.5 mg 등 급여 기준, 용법용량, rivaroxaban (0) | 2020.11.26 |
| Beta blocker(베타차단제), class effect, 심장선택성 (0) | 2020.11.19 |
| epinephrine 개시 시 norepinephrine 용량, NE equivalent dose range (0) | 2020.11.16 |
| Effect of norepinephrine dosage on mortality in patients with septic shock (0) | 2020.11.15 |


댓글