Abstract
목적
CRRT(CVVHDF 모드)를 하는 중증 환자를 대상으로 vancomycin의 약동학적 특성을 조사하고 반코마이신 청소율(clearance)를 파악해보자!
방법
10명의 중증 환자를 대상으로 Vancomycin 750 mg q12h IVF regimen(initial, steady state dose)을 투여 후, 혈액과 ultrafiltrate에서 샘플을 채취하였다.
<CRRT의 setting>
| dialysate | filtration | effluent | blood flow |
| 1 L/hr | 2L/hr | 3L/hr | 200 mL/min |
결과
| CVVHDF clearance of vancomycin | Total VCM body clearance |
clearance of VCM by CVVHDF |
fraction eliminated by all route | sieving coefficient VCM |
| 1.8 ± 0.4 L/hr 30 ± 6.7 mL/min (다른 CRRT mode에 비해서 1.3-7.2 배 큼) |
2.5 ± 0.7 L/hr 41.7 ±11.7 mL/min |
76 ± 16.5 % | 60 % | 0.7 ±0.1 (urea의 경우 0.8 ±0.06) |
토의
- Vancomycin은 CVVHDF에 의해 효과적으로 제거된다.
- clearnace는 다른 mode의 CRRT보다 빠르기 때문에 요구 선량은 상대적으로 커질 수 있다.
- Urea의 clearance를 통한 VCM의 clearance 평가는 이를 과대평가할 수 있다.
CRRT는 HD와 필터의 특성 등이 상당히 다르기 때문에 HD에서의 약제의 약동학적 특성을 가지고 외삽하여 CRRT에서의 약제의 약동학적 특성을 구하는 것은 어렵다. 뿐만 아니라 CRRT의 mode에 따른 차이도 있기 때문에 다른 clearnace를 가진다.
비교적 큰 분자량 때문에 vancomycin은 기존 혈액투석이나 복막투석으로 크게 제거되지 않는다. 최근에는 투과성이 높은 high flux membrame의 도입으로 clearance가 증가하였다. (혈액 투석의 경우 rebound를 고려하여 preHD 농도에 비해 17% 정도 감소됨)
이전 문헌에서의 CRRT시 Vancomycin PK parameter
| Clearance | 11.5-19.3 L/day |
| Vd | 40.9-65.8 L |
한계: 대부분의 연구는 작은 표본 크기, CRRT 셋팅에 대한 정보 부족(dailysate, ultrafiltrate, blood flow rate, haemofilter type, length of therapy, removal of regerence solute such as urea or creatinine)
Methods
- Royal Brisbane Hospital (Queensland, Australia
- From March 2000 to June 2001
- 10 patients were enrolled in the study
- Critically ill patients in whom vancomycin was used to treat a known or suspected infection and who required CVVHDF for acute renal failure of any cause were eligible.
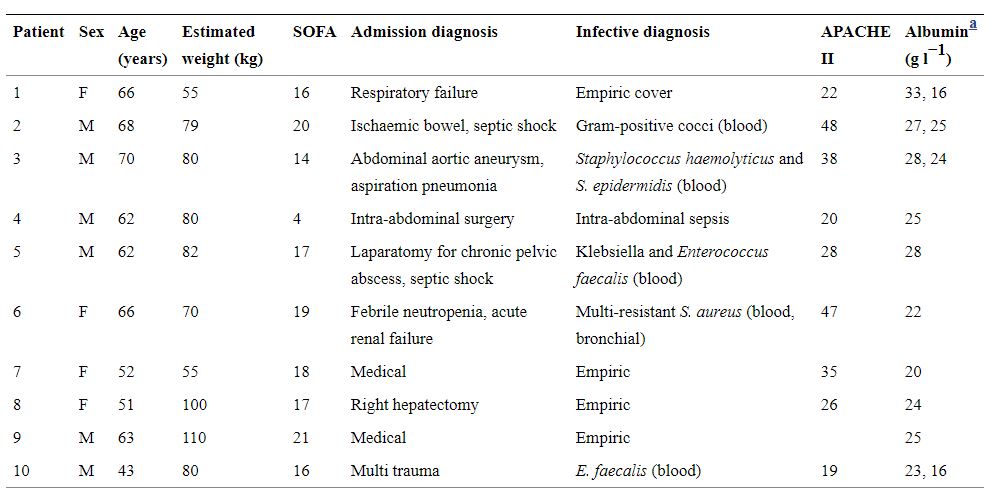
환자별 특징
- blood sample
- indwelling arterial cannula, in heparinized tube
- 첫 샘플(T0, baseline): 750 mg(over 1hr) VCM 투여 직전 via central line
- 이후 샘플: 투여 후 30분(VCM 투여 중), 투여 종료(1hr), 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 hr 후, 매 trough level
- profile A: 치료 첫날 수행된 샘플링으로 얻은 데이터
- profile B: 가능한 경우, 정상 상태(steady state) 도달한 후 3 or 4일 차에 반복된 샘플링으로 얻은 데이터
- 환자 4, 6, 7, 9: LD 1000 mg → 750 mg bid
- 총 15개의 profile 중 8개는 연기기간동안 CVVHDF를 유지하였지만, 1B, 2A, 2B, 5A, 6B, 8A, 10B에서 clotted circuit으로 인해 CVVHDF 중단된 사건이 발생함 = eight of the 15 profiles had CVVHDF for the entire study periods, whereas CVVHDF was interrupted in profiles 1B, 2A, 2B, 5A, 6B, 8A and 10 B due to clotted circuits requiring change.
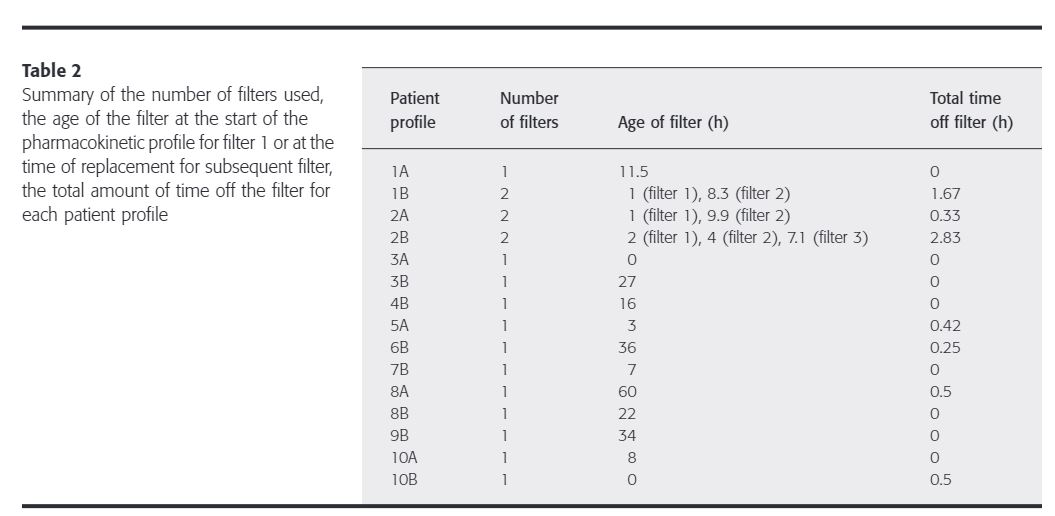
| profile A | initial | 6 | 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 8A, 10A |
| profile B | steady state | 9 | 1B, 2B, 3B, 4B, 6B, 7B, 8B, 9B, 10B |
Urea smaple
- plasma sample collected after 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 hr
- 시간당 effluent 데이터를 이용하여 4시간 간격의 urea clearance 도출
VCM PK data
- tmax and Cmax were directly observed as the maximum measured concentration.
- Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using the WinNonlin software (Pharsight, Mountain View, CA, USA)
- terminal half life: ln(2)/λ₂
- AUC: calculated using the log-linear trapezoidal method.
- AUC₀_₁₂: calculate the AUC extrapolated to infinity (AUC₀_∞) after the first dose (single dose) by the equation ⇛ AUC₀_₁₂ + C₁₂/λ₂
- F₁₂: initial doses the percentage of the dose that was eliminated by all elimination routes during the 12-h study period(12시간동안 투여 용량 대비 제거된 용량 비율) ⇛ 100% × AUC0₀_₁₂/AUC₀_∞
- CL: total body clearance of vancomycin ⇛ dose/AUC₀_∞ (dose; initial dose), dose/AUC₀_₁₂ (dose; subsequent dose)
- Vss: volume of distribution at steady state
- AUC(CVVHDF): In order to calculate the clearance by CVVHDF in profiles where the dialysis was interrupted, the AUC for the period while CVVHDF was in operation, AUC(CVVHDF) was calculated. AUC(CVVHDF) was equal the AUC₀_₁₂, except when CVVHDF was interrupted.
- A(CVVHDF): amount of vancomycin removed by the filter
- CL(CVVHDF): clearance of vancomycin by CVVHDF ⇛ A(CVVHDF)/AUC(CVVHDF)
- F(CVVHDF): 100% × CL(CVVHDF)/CL
Results
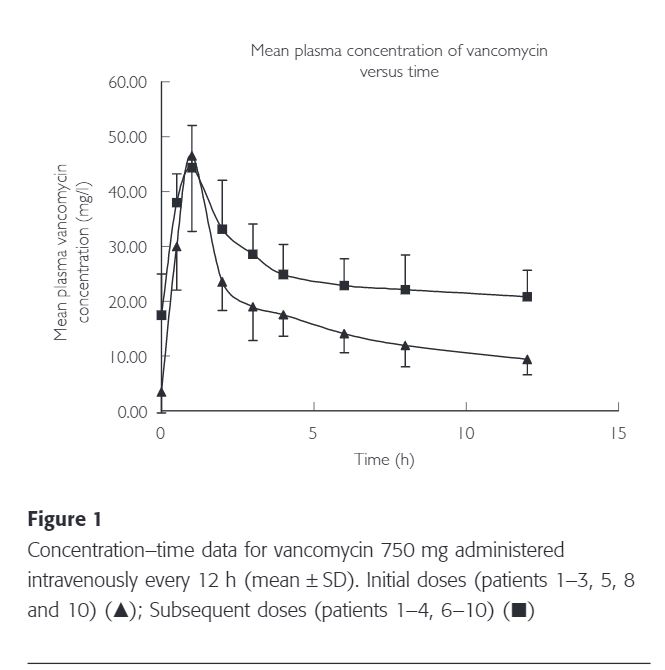
The mean (± SD) plasma vancomycin concentration–time data for the initial and subsequent doses are represented in Figure 1.
Patients 1, 2, 3, 5, 8 and 10 had an initial pharmacokinetic profile (Profile A) taken on commencement of vancomycin therapy. Patients 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 and 10 had subsequent profiles (Profile B) obtained on or after day 3 of therapy.
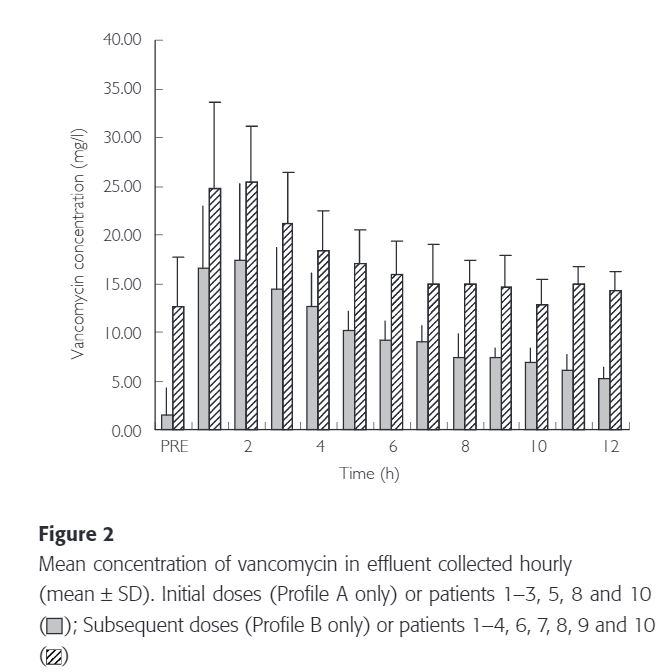
The hourly vancomycin concentration in the ultrafiltrate for both the initial and subsequent doses is depicted in Figure 2.
non-compartment analysis로 가정한 PK parameter(Table 3, 4)
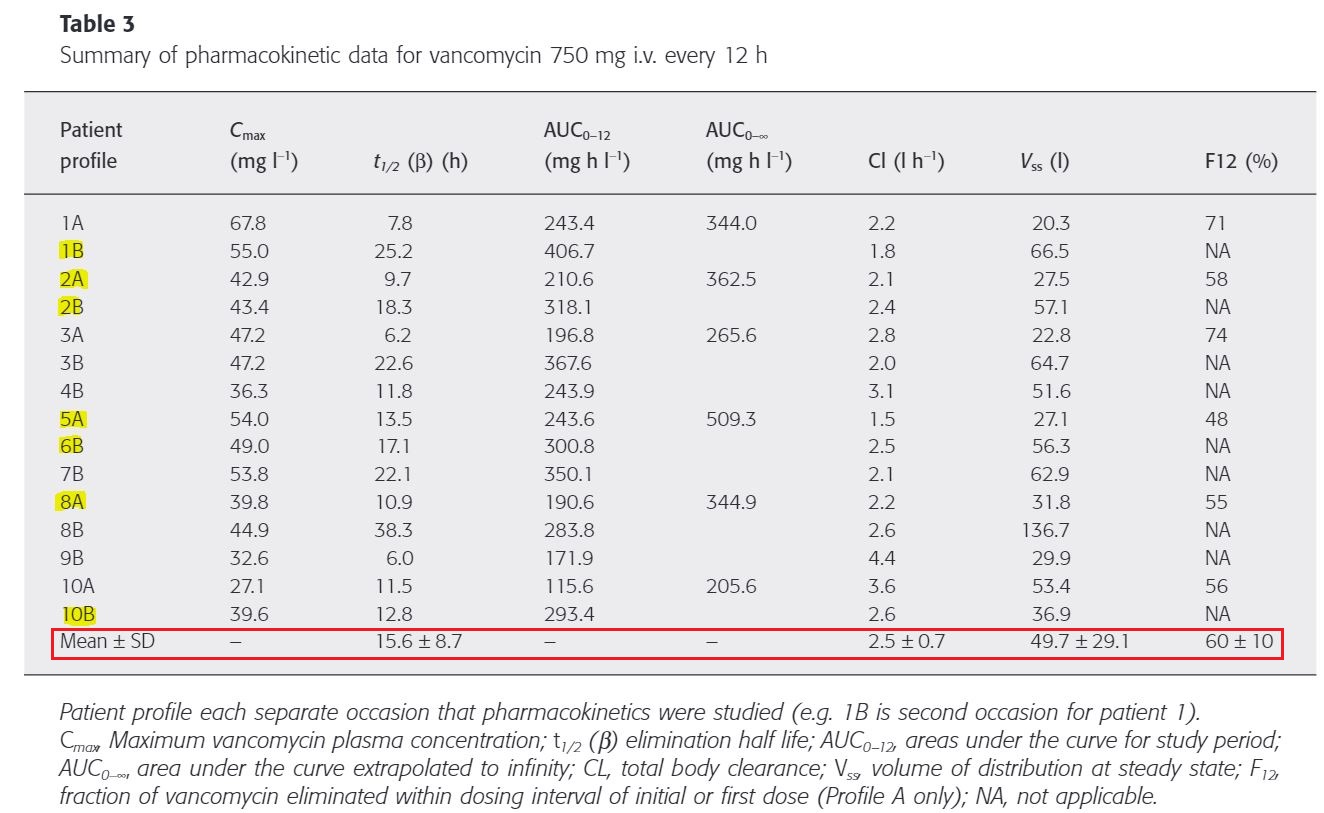
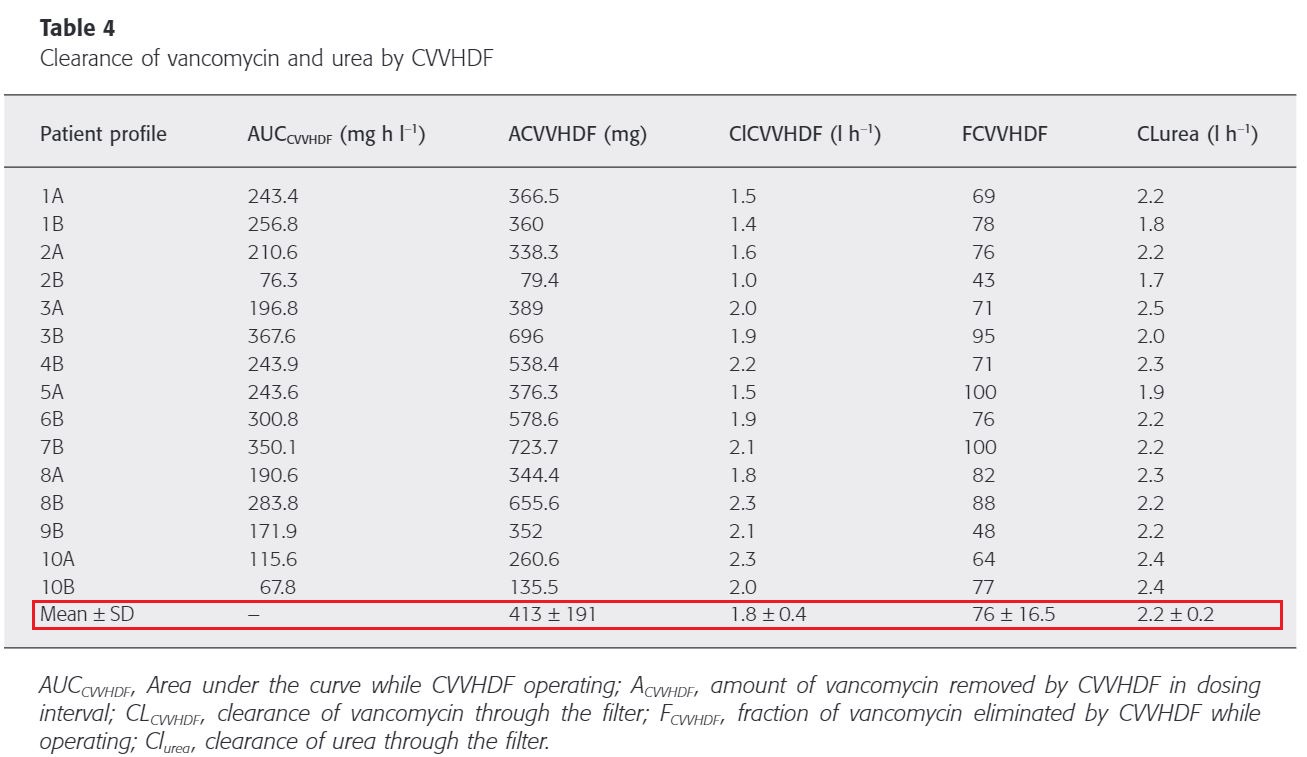
4시간 간격으로 계산된 VCM 또는 urea를 제거하는 필터 성능에는 큰 차이가 없었다. urea의 sieving coefficient는 0.8±0.06이고 VCM sieving coefficient는 0.7±0.10으로 urea에 비해 더 낮고 더 가변적이다.
따라서 urea를 이용하여 VCM의 대략적인 제거 인자로 사용할 수 있다.
Discussion
이 연구의 결과 CVVHDF동안 반코마이신이 효과적으로 제거된다는 것을 보여준다. 이는 이전의 연구와 일치하는 결과이다. 이 연구에서는 CVVHDF 12시간 동안 반코마이신의 선량의 절반 이상이 제거되었음을 보여주었다.
Extracorporeal elimination이 total body clearance의 25-30%가 초과될 때 임상적으로 유의하게 영향을 끼친다는 연구 결과를 토대로 CVVHDF 시, total body clearance에 함께 고려해야 한다.
| total | CVVHDF | |
| Clearance | 2.5±0.7 41.7±11.7 mL/min(30-53.4 mL/min) |
1.8±0.4 30±6.7 mL/min |
Sieving coefficient란 ultrafiltrate와 plasma의 약물 농도 비이며 heamofilter의 투과성을 의미한다. 연구를 통해 도출된 반코마이신의 평균 sieving coefficient은 0.7±0.10로써 이전에 문헌적으로 보고된 값과 일치된 결과이다. sieving coefficient는 막을 사용하는 시간이 지남에 따라 감소할 수 있지만 해당 결과는 controversial 하다. CVVHDF의 성능은 12시간 연구기간 동안 4시간 간격으로 평가되었고 큰 변화는 없었다.(Table 3)
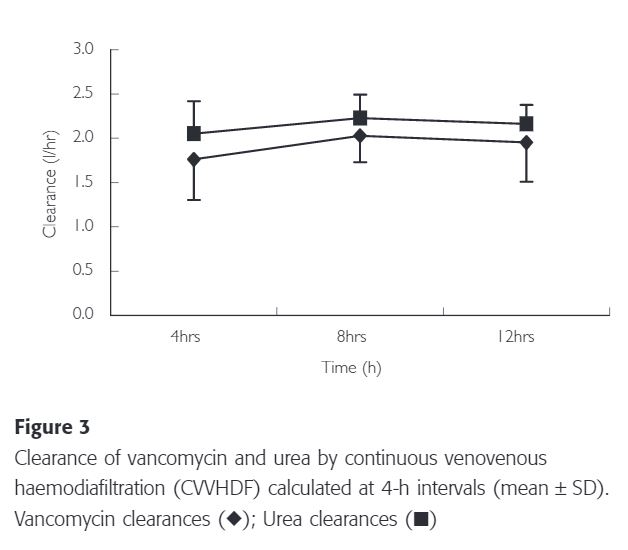
뿐만 아니라 단백 결합의 변화에 따라 sieving coefficient에 영향을 끼칠 수 있다. 그 밖에 blood pH, albumin, protein, bilirubin, heparin 사용, TPN, fat emulsion 등이 영향을 끼친다. 이는 이전에 보고된 urea coefficient 값의 차이의 이유가 설명될 수 있다.(0.8±0.06 vs. 0.83±0.06)
환자 8의 경우 38.3 hr의 반감기를 나타내었는데 이는 환자의 심각한 간질환/신질환으로 인한 것으로 예상되며 이전의 연구 결과에서도 비정상 간 기능을 가진 환자의 VCM 반감기 연장이 보고된 바 있다.
본 연구에서 측정된 Vss는 49.7±29.1L로 이전에 보고된 47.3±6.4L와 일치됨을 보여준다. 이를 체중당 분포 용적으로 나타날 때 0.65±0.36L/kg로 정상 신장 기능을 가진 성인 환자에 대해 보고된 범위 내에 있었다. 예외적인 경우는 136.7 L(1.4 L/kg)를 가진 환자 8의 결괏값인데, 이는 fluid overload or unstable state를 반영한 값이라고 볼 수 있다. 따라서 이러한 임상적으로 불안정한 환자에서는 진정한 staedy state의 농도를 달성하기 어려울 수 있다.
In conclusion, vancomycin is cleared effectively by this method of continuous venovenous haemofiltration. The clearance appears to be faster than that of other forms of continuous renal replacement therapy. A dose of 750 mg intravenously every 12 h provided adequate serum concentrations for the critically ill patients in this study, but accumulation occurred. The dose may need to be reduced over the longer term, as only approximately 60% of a dose was cleared over a 12-h period.
To achieve an average steady-state concentration of 15 mcg/mL and using the clearance of 2.5 L/hr, a maintenance dose of 450 mg of vancomycin every 12 h would be required.
reference:
1) DelDot, Megan E., Jeffrey Lipman, and Susan E. Tett. "Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in critically ill patients receiving continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration." British journal of clinical pharmacology 58.3 (2004): 259-268.
'👩⚕️Px 영역 > TDM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Vancomycin TDM: pks 프로그램, Abbott 프로그램을 이용한 AUC 계산, linear/logarithmic trapezoidal AUC calculation (9) | 2021.10.29 |
|---|---|
| 디곡신(Digoxin) TDM therapeutic range, 심부전, 심방세동 (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| 디곡신 농도 채혈 시간? digoxin TDM sampling time (0) | 2020.10.26 |
| Vancomycin AUC calculator, bayesian model, TDM software ; DoseMeRX (6) | 2020.09.21 |
| Vancomycin TDM, software program, Bayesian method (4) | 2020.07.17 |


댓글