경구로 섭취하기 힘든 소아, 신생아, 미숙아에게서는 정맥 영양(Parenteral nutrition; PN)으로의 영양 공급은 매우 중요한 요인이다. 지질(lipid injectable emulsion)을 포함한 PN의 요소들은 빛에 노출되어 산화될 수 있다.(photo-oxidation) 광분해 생성물은 산화 스트레스(oxidative stress)에 노출되고 이는 성인에 비해 소아가 더 취약하다.
Oxidative stress → bronchopulmonary dysplasia, retinopathy of prematurity, necrotizing enterocolitis, and intestinal failure–associated liver disease
이번 ASPEN(The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition)에서 PN의 광보호(photoprotection)에 대해 권고사항을 발표하였다.(Position Paper)
이번 발표에는 빛에 노출 후 정량 가능한 과산화물 및 기타 분해 산물의 형성에 관한 문헌을 검토하여 해당 PN에 노출된 미숙아에서의 좋지 못한 임상 결과를 평가하였다. 실제 임상적으로 완벽한 광분해를 예방할 수 없겠지만 실천 가능한 관행을 고려해보고 그 시도에 의의를 두고자 한다.
개요
- Peroxide formation in parenteral nutrition (PN) admixtures occurs when lipid injectable emulsions (ILEs), amino acids, vitamins, and trace elements are exposed to ambient light and phototherapy.
- Premature infants appear to be most susceptible to consequences of peroxide formation in PN admixtures because of immature defense mechanisms and several conditions associated with oxidative stress (eg, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, necrotizing enterocolitis, and retinopathy of prematurity).
- Failure to protect PN admixtures (both ILE-free and ILE-containing) from light exposure can increase the generation of peroxides as well as by-products of lipid peroxidation.
- Complete PN photoprotection from light (bag plus infusion sets) is more effective than partial photoprotection (bag only) in reducing markers of oxidative stress.
- Based upon the best available evidence, the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) recommends complete PN light protection beginning as soon as possible during the PN compounding process and continued until the entire PN admixture and ILE infusion is complete.
- Individual healthcare organizations should convene key stakeholders to define which steps in PN photoprotection can be achieved and implement such strategies.
ASPEN and the authors understand that the full implementation of complete photoprotection may not currently be feasible given current product availability; recommendations provided in this paper serve to represent the goal to which to strive as well as to highlight the importance of product availability to achieve these practices.
미숙아를 포함한 PN이 필요한 소아 집단에서 PN을 통한 영양 공급의 이점에도 불구하고 PN 성분이 산소 하 빛에 노출되었을 때 광분해 산화된다는 근거가 증가하고 있다. 광분해 산화는 PN의 여러 성분 중 특히 비타민과 지질 성분이 더 취약하다. 모든 광원에서 분해가 발생하지만 특히 자외선 영역에서 더 취약하다.
분해 산물로는 lipoperoxide & ascorbylperoxide가 있다.
산화 스트레스를 측정하는 바이오마커로는 malondialdehyde, redox potential of glutathione, isoprostanes, and dityrosine 등이 있다.
2019년 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA)에서 차광이 이루어지지 않은 비타민, 미량원소, 아미노산, 지질 등이 혼합된 제형을 투여하였을 때 유아 환자에게서 부작용에 대한 보고를 평가 후 잠재적으로 심각한 부작용이 나타날 수 있음을 인정하였다.
Implementation of PN photoprotection with available equipment
| Process | Potential for error/harm | Proposed solution |
| 각각의 용기에 차광(amber) 스티커 부착 | 잘못된 라벨이 부착될 수 있음 | 이 단계에서 라벨을 부착하지 않기 라벨을 볼 수 있도록 부착하기 |
| 투여 전 라벨 검토를 위해 차광 커버 제거 | 차광 커버를 다시 씌우는 단계에서 다른 환자의 커버로 바뀔 수 있음(ex. 미처 폐기되지 않은 다른 환자의 차광 커버) | 필요 부분만 절단하기 |
| 투여 기간동안 차광 커버 씌우기 | 유화액의 상태(particulates, cracked emulsion)을 검사할 수 없음 | - |
| 차광 커버가 없거나 차광 가능한 주입 펌프가 없을 경우 기타 재료(ex. 알루미늄 호일)을 씌우기 | 유화액의 상태(particulates, cracked emulsion)을 검사할 수 없음 알루미늄 호일 등을 사용 시 틈새가 발생할 수 있음 |
차광 튜브 고려하기 온도를 상승시킬만한 물질 피하기 |
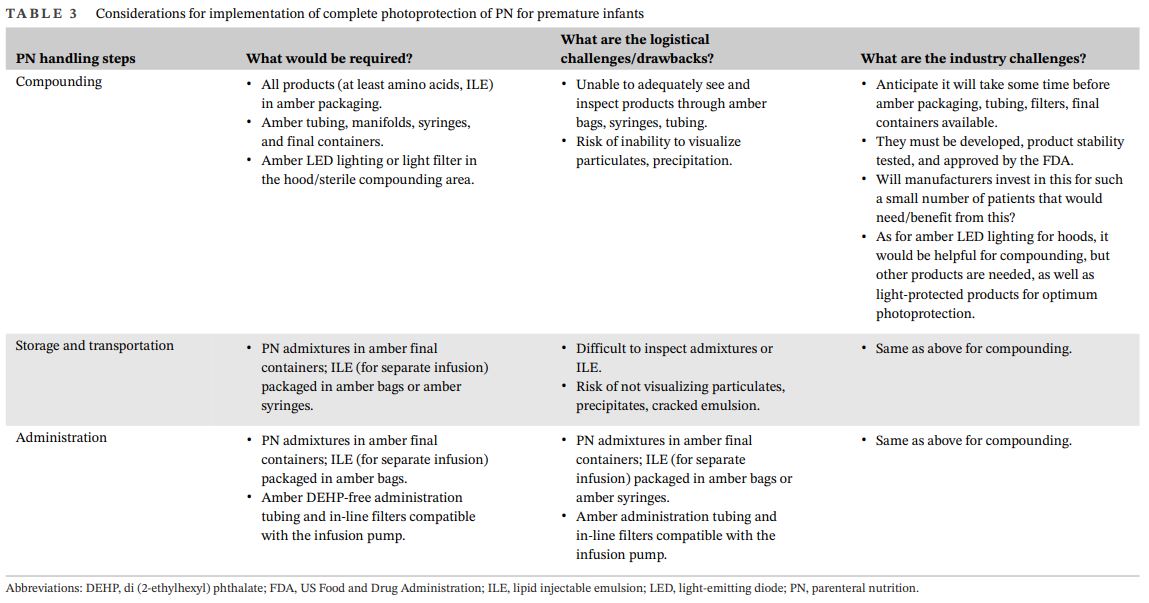
Considerations for implementation of complete photoprotection of PN for premature infants
SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- In vitro testing indicates PN and ILE integrity, including precompounding individual components as well as the final admixture, is optimized with light protection. Light exposure at any step in storage, compounding, delivery, and infusion can alter the admixture stability.
- In vitro data indicate that partial photoprotection of PN products reduces markers of oxidative stress, although it is not as effective as complete photoprotection.
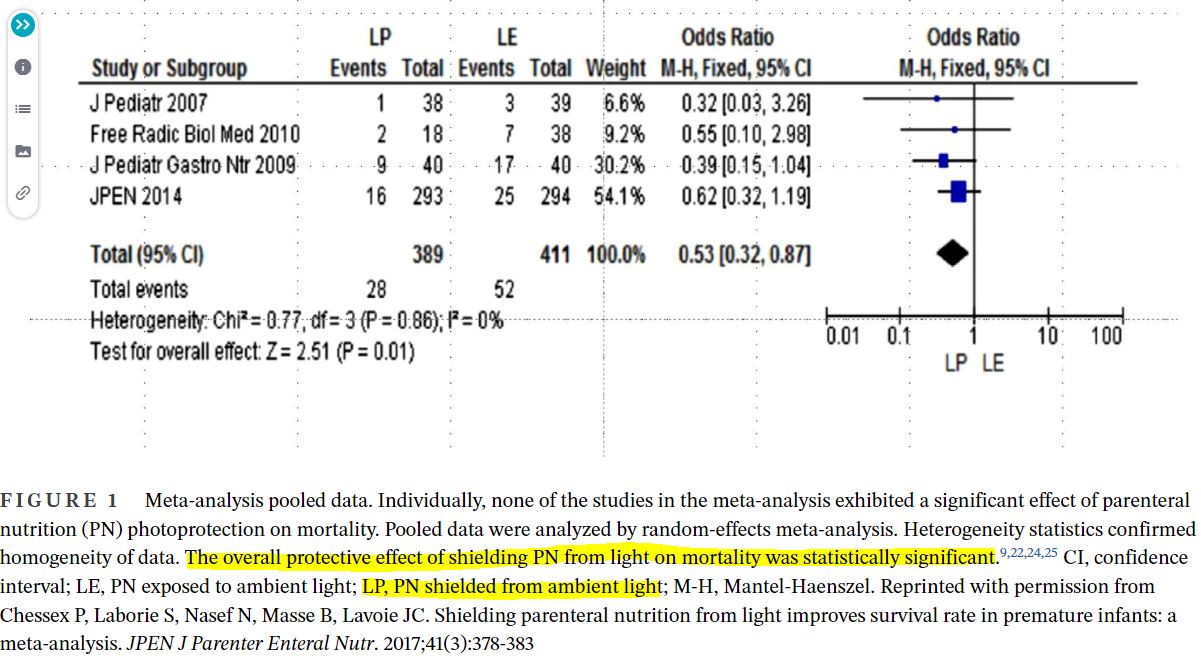
- Data from clinical trials, evaluated individually and collectively in a meta-analysis, suggest complete photoprotection of PN admixtures and ILEs reduces indicators of oxidative stress in preterm infants and mitigates the risk of adverse clinical outcome measures. It remains noteworthy that statistically significant findings of benefit from light protection were sometimes found only with secondary analysis. No harm was identified as a result of photoprotection.
- Materials required for complete photoprotection from the moment PN compounding is initiated in the pharmacy are not currently available in the US, yet materials are currently available for partial photoprotection.
- ASPEN recommends photoprotection of PN admixtures and ILEs for infants. Insufficient literature exists to inform recommendations surrounding photoprotection of PN admixtures and ILE administered to older children or adults. However, sufficient evidence suggests that PN components utilized in children and adults are susceptible to photo-oxidation.
- Individual healthcare organizations should convene key stakeholders to define which steps in photoprotection can be achieved and implement such strategies. (각 센터에 맞는 차광법을 고려해보아야 한다.)
- Outsourcing sterile compounding facilities should review processes that may be amenable to reducing light exposure, both during the compounding process as well as during the transport process.
- Research and development of cost-efficient materials are necessary for complete photoprotection of PN admixtures and ILEs.
- ASPEN and the authors understand that the full implementation of complete photoprotection may not currently be feasible given current product availability; recommendations provided in this paper serve to represent the goal to which to strive as well as to highlight the importance of product availability to achieve these practices.

reference:
1) Robinson, Daniel T., et al. "Recommendations for photoprotection of parenteral nutrition for premature infants: An ASPEN position paper." Nutrition in Clinical Practice 36.5 (2021): 927-941.
'👩⚕️Px 영역 > TPN·영양' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 간경변 환자(cirrhosis), ESPEN, PN, EN, 지질 제한, 단백 제한 (0) | 2022.01.17 |
|---|---|
| Insulin: TPN 중 insulin, dextrose 당 insulin 투여량, 고혈당(hyperglycemia) (3) | 2022.01.13 |
| ASPEN, lipid 제제 권고사항, 필수지방산 결핍 예방, essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD) (1) | 2022.01.04 |
| 간경변증(liver cirrhosis) 환자의 영양 치료, nutrition, ESPEN guildeline (0) | 2021.11.03 |
| 비만 환자에서의 nutrition, obesity, ASPEN, ESPEN, hypocaloric, high protein 식이 (0) | 2021.10.28 |


댓글