
국내 허가사항
이론적 요구량에 따라 결정된 투여량을 염화나트륨으로서 시간당 100mL 이하의 속도로 천천히 점적 정맥 주사하되, 24시간 동안 400mL를 초과해서는 안된다.
투여량, 투여 속도는 연령, 체중, 증상에 따라 적절히 증감한다.
투여하는 동안 체액 및 전해질 평형을 모니터링해야 한다.
저나트륨혈증(hyponatremia)
고농도 염화나트륨액은 증상이 동반된 저나트륨혈증에 효과적인 치료 방법이다.
교정 속도가 너무 느리면 뇌부종을 예방하기에 부족할 수 있으며 반면 교정 속도가 너무 빠를 경우 osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS)와 같은 영구적 신경 장애가 발생할 수 있다.
이러한 우려로 마라톤 선수의 저나트륨혈증 치료를 위해 고삼투 식염수(intermittent use of a bolus of hypertonic saline)의 간헐적 주입 개념은 2005년에 도입되었다.
최신의 미국과 유럽의 가이드라인에서 소규모의 RCT, 케이스 리포트 등의 결과를 바탕으로 small/fixed boluse의 고삼투 식염수의 투여를 권장하고 있다.
고정 용량의 투여는 다음과 같은 이점이 있다.
(1) efficacy: 신속한 혈청 나트륨 교정
(2) safety: 지속 주입에 비하여 과도한 보정 위험이 낮음
(3) user friendly: 계산 필요성이 없음
하지만 slow continuous infusion (SCI) therapy vs rapid intermittent bolus (RIB) therapy 중 어느 치료 방법이 더 최선인지에 대한 명확한 증거는 없다. 이버 연구에서 중증 증상이 있는 저나트륨혈증 환자를 대상으로 각 치료 방법의 효능과 안전성을 비교하였다.
Prospective, investigator-initiated, multicenter, open-label, randomized clinical trial that was performed in 3 general hospitals in Korea.
환자군
Moderately severe to severe symptoms & glucose-corrected sNa < 125 mmol/L
* Moderate symptoms include nausea, headache, drowsiness, general weakness, and malaise
* Severe symptoms include vomiting, stupor, seizure, and coma (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] score ≤8)
| a | b |
| rapid intermittent bolus (RIB) therapy | slow continuous infusion (SCI) therapy |
| 3% saline 2 mL/kg over 20 min X 1회 or 3% saline 2 mL/kg over 20 min X 2회 |
3% saline 0.5 mL/kg/hr or 3% saline 1 mL/kg/hr |

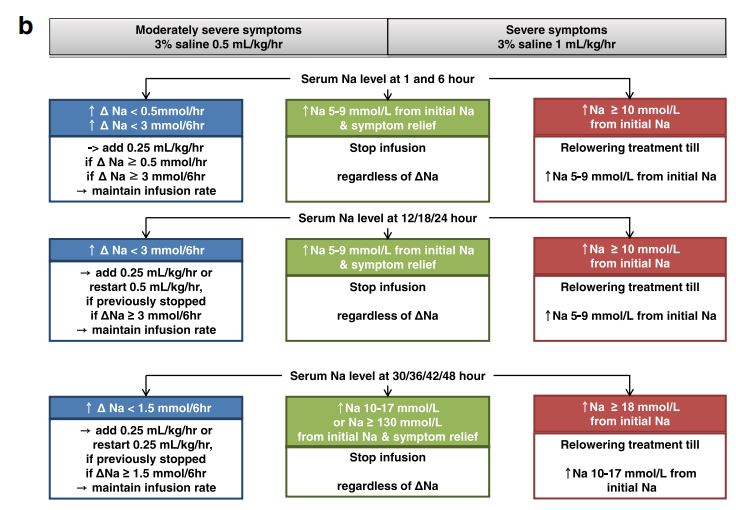
치료 목표; 24 시간 이내 serum Na 5-9 mmol/L 상승 & 48시간 이내 10-17 mmol/L 상승 or 150 mmol/L 이상 도달
각 smple time마다(2일 동안 6시간마다) 과보정을 체크하고 과보정 시 relowering treatment을 시행함(dextrose, 5%, infusion of 10 mL/kg over 1 hour and/or intravenous desmopressin 2 µg if sNa level increase was ≥10 mmol/L within the first 24 hours or ≥18 mmol/L within 48 hours)

두 군 간 과보정 발생률(over-correction rate)에서 유의한 차이는 없었다.(15% vs 22%, p=0.26)
RIB군은 SCI군에 비해 재저하 치료(relowering treatment) 비율이 낮았다.(36% vs 52%, p=0.04)
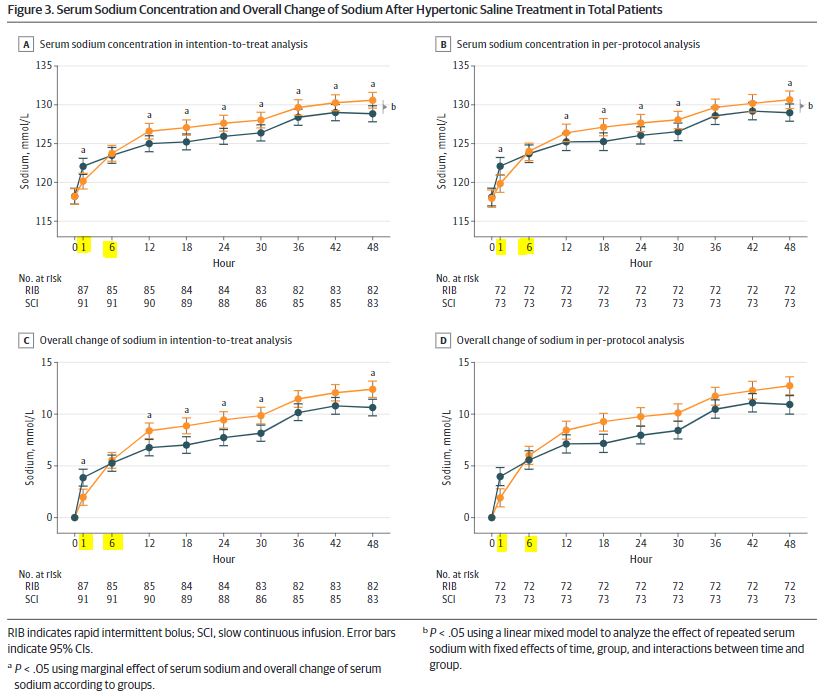
RIB는 SCI보다 1시간 이내 목표 보정률*이 높은 경향을 보였지만 6시간 치료 후 효능 면에서는 차이가 없었다.
*serum Na 5-9 mmol/L 달성
즉, 1 시간 이내 목표 도달 환자 비율이 RIB 군에서 더 높은 경향을 보이는 것은 RIB군에서 1시간, 6시간 이내 투여한 고장성 식염수 양이 더 많았던 점을 감안하면 RIB 치료 효과가 더 좋을 수도 있다.
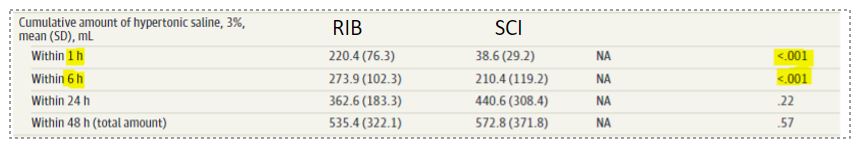
RIB 치료 방법은 SCI에 비해 처음 1시간 이내 목표 보정률을 달성하는데 효과적인 경향이 있고 과잉 보정 위험이 증가하지 않았으며 계산이 필요 없어 사용자 친화적인 방법이다. 게다가 나트륨의 빠른 보정에도 불구하고 환자들 중 누구도 ODS가 나타나지 않았다. 이러한 이유로 저나트륨혈증 환자에서 RIB 치료가 권장될 수 있다.
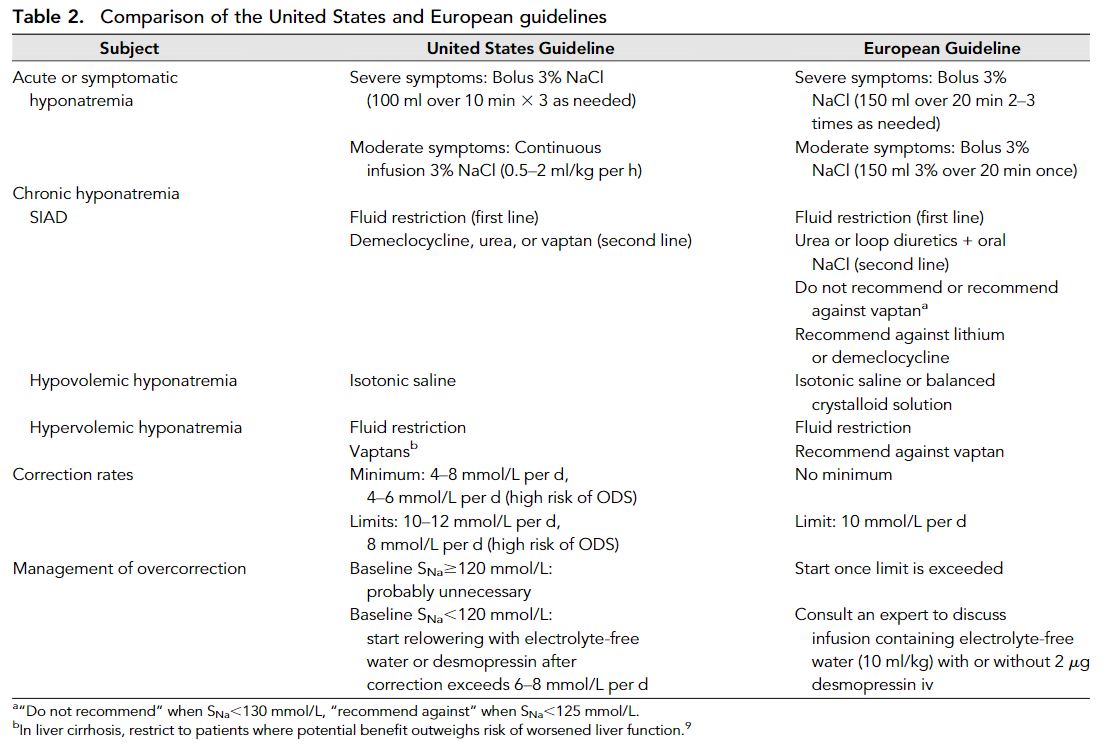
한국인은 미국이나 유럽인에 비해 체격이 작은 경향이 있기 때문에 3% NaCl 100-150 mL의 고정된 용량을 투여하지 않고 체중 기반 접근법이 권장된다.
최근 가이드라인에서는 serum Na가 5 mmol/L 증가와 증상 개선이 보이면 고장성 NaCl의 주입을 중단할 것을 권고하고 있다.
Conclusion
To our knowledge, the SALSA trial is the first prospective, multicenter, randomized, open-label clinical trial to compare the efficacy and safety between RIB and SCI with hypertonic saline in patients with moderately severe or severe symptomatic hyponatremia. Both RIB and SIC therapies of hypertonic saline for treating hyponatremia were effective and safe, with no difference in the overcorrection risk. However, RIB therapy had a lower incidence of therapeutic relowering of sNa and tended to have a better efficacy in achieving sNa within 1 hour than SCI. RIB therapy could be suggested as the preferred treatment of symptomatic hyponatremia, which is consistent with the current consensus guidelines.
🙄 국내 허가사항에서는 3% NaCl의 최대 투여 속도를 100 mL/hr로 권고하고 있지만 최근 가이드라인 등에 rapid intermittent bolus 방법(3% saline 2 mL/kg over 20 min)이 권장될 수 있다.
recent guildeline
유럽 : Spasovski G, Vanholder R, Allolio B, et al; Hyponatraemia Guideline Development Group. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014;170(3):G1-G47.
미국 : Hoorn EJ, Zietse R. Diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia: compilation of the guidelines. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(5):1340-1349.
reference:
1) Baek, Seon Ha, et al. "Risk of overcorrection in rapid intermittent bolus vs slow continuous infusion therapies of hypertonic saline for patients with symptomatic hyponatremia: the SALSA randomized clinical trial." JAMA internal medicine 181.1 (2021): 81-92.
2) 약학정보원


댓글