집중 치료가 필요한 ICU 환자들의 대부분은 동맥 카테터(arterial catheter)를 이용하여 동맥혈압을 측정하거나 채혈을 하는 데 이용한다. 이러한 카테터의 개방성(patency)을 유지하여야 정확한 측정값을 확보할 수 있고 카테터가 막혀서 교체하는 비용을 줄일 수 있다.
Uncertainty exists amongst clinicians as to best practice surrounding the contents of the arterial catheter flush solution (heparin or saline). The use of heparin is more expensive and is accompanied by significant risks such as haemorrhage, hypersensitivity and heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
A-line 개방성 유지를 위하여 heparin을 사용함으로써 출혈, 과민성, HIT 등의 위험이 높아질 수 있다.
헤파린의 항응고 특성을 이용하여 동맥 카테터 내부의 혈액이 응고되는 것을 방지하는 수단으로 이용하였다. 이 양은 아주 적지만(ex. A patient who receives the minimum dose of heparin flush solution of 1 IU/h plus a 5‐mL flush/h following hourly arterial blood gas analysis will receive approximately 192 IU of heparin/24 h.) 헤파린의 이상 반응 위험이 아예 없는 것은 아니다.
Following publication of the results of the 1998 systematic review and meta‐analysis performed by Randolph and colleagues, normal saline flush has replaced heparin as the standard flush solution for peripheral venous catheters in most clinical settings (Randolph1998).
1998년 발표된 체계적/메타 분석 결과 말초 혈관 카테터의 표준 플러싱 용액으로써 헤파린 용액에서 생리식염수로 대체되었다.
However, the use of 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline) as an arterial flush solution, with or without heparin, to minimize thrombus formation and prolong the patency of the catheter began before any research was conducted to determine its efficacy in this setting (Randolph1998; Tuncali 2005).
Over the years, numerous research projects have been conducted with varying and sometimes contradictory outcomes (de Neef 2002; Randolph1998).
Hence clinicians remain uncertain as to best practice surrounding the use of heparin or normal saline as a flush solution for maintaining the patency of arterial catheters.
코크란 리뷰의 목적은 NS와 heparin을 비교하였을 때 혈액학적 이상반응 없이 환자의 카테터 개방성을 유지함에 있어 안전성과 효능을 평가하기 위함이다.
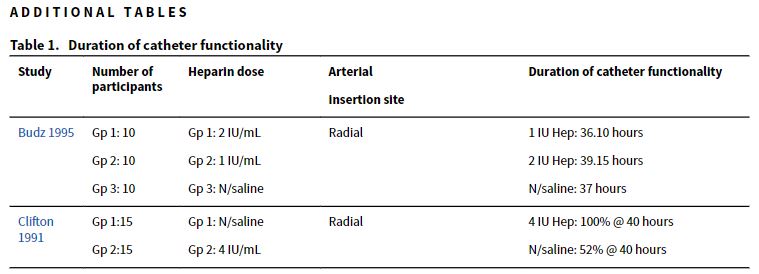
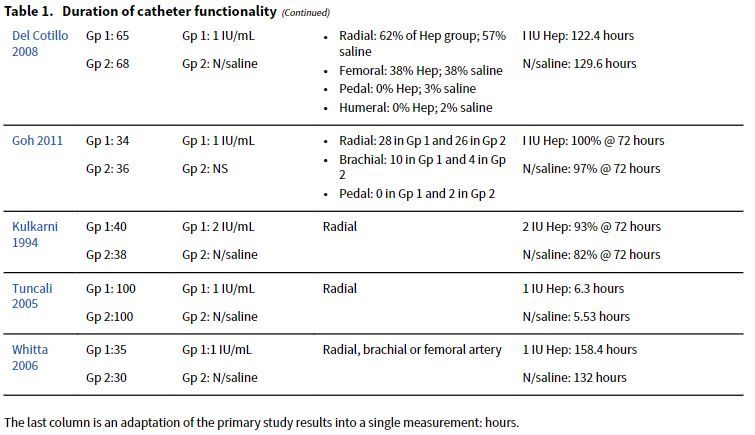
총 7개의 연구(606 명)가 inclusion criteria를 만족하였다.
지속적인 압력 하에서 1-2 IU/mL 농도의 heparin을 이용한 개별 연구의 결과는 부정확했으며 차이에 대한 결정적인 증거를 제공하지 못했다. 마찬가지로 혈종(hematoma), 삽입 부위 감염, 허혈증과 같은 이상 반응 평가와 보고의 일관성이 낮았다. 일반적으로 사용되는 heparin 농도를 계층화한 추가 연구가 필요하다.
결론(Authors' conclusions)
The available evidence is of poor quality because of risk of bias and does not provide sufficient information to support the effects of adding heparin (1 to 2 IU/mL) to a maintenance solution (pressurized to deliver 3 mL of flush solution per hour) of 0.9% normal saline in maintaining the patency and functionality of arterial catheters.
reference:
1) Robertson‐Malt, Suzanne, et al. "Heparin versus normal saline for patency of arterial lines." Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 5 (2014).
'🤹♂️ 카테고리별 약물 > 기타' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Amantadine의 특징, 외상성 뇌손상 환자, traumatic brain injury (0) | 2022.05.21 |
|---|---|
| 아스피린 및 비스테로이드성 항염증제(NSAIDs계 소염진통제) 과민 반응, Hypersensitivity (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 식약처: 필터 수액세트 안전성 정보 관련 권고사항: 프라이밍 방법 (0) | 2022.01.26 |
| DIC(disseminated intravascular coagulation) 진단, 약물 치료(diagnosis, treatment) (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| 재생불량성 빈혈, cyclosporine 복용 시 주의사항 (1) | 2021.12.08 |


댓글