CVC(central venous catheter)나 PICC(peripherally inserted central catheter)의 장기간 사용은 해당 부위의 감염의 위험 증가 즉, CRBSI(catheter-related bloodstream infection)으로 이어진다. 카테터 내부에 군집된(colonized) 병원성 미생물을 쉽게 생체막(biofilm)을 형성되고 이는 약물 투입 등의 행위로 인해 혈류로 확산될 수 있다.
카테터 공간에 고농도의 항생제를 거치하여 형성된 생체막을 녹여 세균의 군집을 줄이고 세균의 박멸을 유도할 수 있는 antibiotic-lock therapy가 개발되었다.
☝ 관류(flushing)?
- 부적합성(imcompatibility) 약물이 섞이는 것을 예방하고 혈액이나 섬유소를 정맥관 내강에서 씻어내는 방법
- 관류 최소 용량은 정맥관과 부속기구를 합한 정맥관 내부 용적의 2배
- ex) 말초정맥관 5 mL, 중심정맥관 10-20 mL
☝ 잠금(locking)?
- 정맥관을 사용하지 않을 때 정맥관 내강으로 혈액이 역류하여 정맥관이 막히는 것을 방지

다음은 근거기반 임상간호실무지침의 권고안이다.

📌 잠금용액(lock solution)
중심정맥관의 잠금용액: 10 IU/mL heparin or normal saline
- 효과 비용 면에서 두 방법의 유의한 차이가 없다.
- 헤파린은 정맥관 내에서 혈액 응고를 방지하여 최저 농도 헤파린(10 IU/mL)을 최소량 사용해볼 수는 있으나 생리식염수보다 우월하다는 근거는 없다.
- 10 IU/mL vs 100 IU/mL 헤파린 용량에 따른 중심정맥관 폐색 발생률 차이가 없다.
- 잠금용액에 사용한 heparin에 의해 HIT(heparin induced thrombocytopenia)가 발생할 수 있다.
잠금용액 양
- 정맥관 내부 전체를 채울 수 있을 만큼 충분한 양이어야 한다
- 정맥관의 내부 용적은 비교적 적은 편이다.
- 잠금 용액이 누출될 가능성이 있으므로 정맥관과 부속기구의 내부 용적보다 15-20% 이상 많은 양이 필요
TIP
- 중신정맥관을 잠글 때 정맥관에 적당한 양압을 가하지 않으면 혈액이 정맥관 내강으로 역류된다. 따라서 마지막 순간까지 용액을 주입하면서 양압 상태를 유지한 채 클램프를 잠근다.

BMC pediatrics 21.1 (2021): 1-10.
NICU에 입원한 조산아를 대상
PICC 배치 후 첫날부터 매일 3회간(q8h) antibiotic-lock therapy가 수행되었음
| vancomycin-lock group | control group |
| heparin plus vancomycin | heparin only |
| 0.5 mL lock solution |
|
| 10 IU/mL heparin + 25 μg/mL vancomycin |
10 IU/mL heparin |
| 각 잠금 장치에 대해 용액을 30분 동안 유지한 후 식염수 2 mL를 이용하여 flush한다. For each lock, the lock solution was retained for 30 min and was then discarded and flushed away from the catheter with 2 ml of normal saline, followed by addition of the former solution used in the catheter. |
|
| The incidence rate of CRBSI 4.4%, 3/68 |
The incidence rate of CRBSI 21.7%, 15/69 |
Clinical infectious diseases 49.1 (2009): 1-45.
Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intravascular catheter-related infection
WHAT IS ANTIBIOTIC LOCK THERAPY AND HOW IS IT USED TO TREAT PATIENTS WITH CATHETER-RELATED INFECTION?
CRBSI 환자의 경우 항생제 잠금 장치 단독으로 사용해서는 안되고 전신 항생제 요법을 10-14일간 투여해야 한다.
항생제 잠금 용액 유지 기간(Dwell times for antibiotic lock solution)은 일반적으로 48시간을 초과하지 않아야 한다. 대퇴부 카테터의 경우 24시간마다 교체할 것을 권장한다. 투석환자의 경우 투석 때마다 교체할 수 있다.(patients who are undergoing hemodialysis, the lock solution can be renewed after every dialysis session)
| CRBSI due to S. aureus and Candida species |
다른 부위에 카테터를 거치할 수 없는 상황과 같은 특별한 경우를 제외하고 항생제 잠금 치료를 시행하는 것보다 카테터 제거(infection source control)을 더 권장한다. |
| 카테터 culture: coagulase-negative staphylococci or gram-negative bacilli peripheral blood culture: no growth |
항생제 잠금 치료 +전신적 항생제 치료 10-14일 |
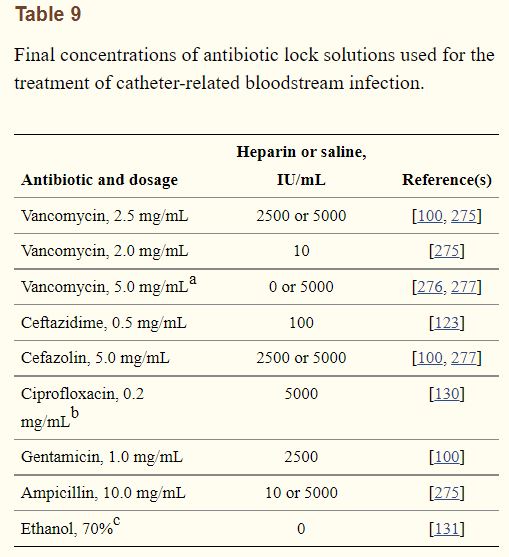
a Vancomycin 농도가 5 mg/mL일 때 1 mg/mL에 비해서 staphylococci에 의한 생체막 제거에 더 효과적이었다. vancomycin 10 mg/mL와 heparin 10,000 IU/mL 희석액에서 침전이 유발되었다. 하지만 약 10초간 흔들었을 때 침전물을 사라졌으며 37도에서 72시간 동안 사라진 상태로 유지되었다.
2500 IU/mL heparin + 5 mg/mL vancomycin 만드는 방법
The lock solution in 2500 IU/mL heparin can be made as follows: using vials containing 50 mg/mL of vancomycin in water, remove 2 mL and dilute in 8 mL 0.9% NaCl, resulting in 10 mg/mL of vancomycin. Place 1 mL of 5000 IU/mL heparin in a glass test tube and mix with 1 mL of the 10-mg/mL vancomycin solution (B. J. Rijnders and R. Mathot, personal communication).
| 재구성 : 250 mg 반코마이신 바이알 + SWI 5 mL = 재구성 후 농도 50 mg/mL |
5000 IU/mL 헤파린 (희석 필요 없음) |
| 재구성 용액 2 mL + NS 8 mL = 농도 10 mg/mL |
|
| 1 mL 취함 | 1 mL 취함 |
| 총 2 mL = 반코마이신 최종 농도 5 mg/mL, 헤파린 최종 농도 2500 IU/mL |
|
** 국내 헤파린 제형은 1000 IU/mL or 5000 IU/mL 두 가지 농도가 있다. 각각의 농도에서 다양한 총 부피로 출시된다.(ex. 10 cc, 5 cc, 20 cc 등)


b 0.2 mg/mL보다 고농도에서 ciprofloxacin은 침전을 일으켰다. (최대 희석 농도 ciprofloxacin : 0.2 mg/mL)
c in-vitro 연구에서 70% 에탄올과 실리콘 or polyetherurethane 카테터의 적합성이 밝혀졌다.
위의 antibiotic lock solution은 해당 농도에서 침전을 일으키지 않을 것이다.
cefazolin은 methicillin-susceptible staphylococci에, vancomycin은 methicillin-resistant staphylococci에 선호된다.
ceftazidime, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin은 그람 음성균에 사용될 수 있다.
ampicillin은 ampicilli sensitive enterococcus에, vancomycin은 ampicillin resistant enterococcus(not VRE)에서 선호된다.
reference:
1) Mermel, Leonard A., et al. "Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intravascular catheter-related infection: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America." Clinical infectious diseases 49.1 (2009): 1-45.
2) uptodate
3) Liang, Hong, et al. "Vancomycin-lock therapy for prevention of catheter-related bloodstream infection in very low body weight infants." BMC pediatrics 21.1 (2021): 1-10.


댓글